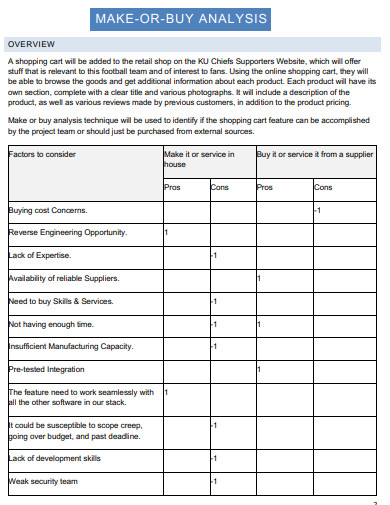
Project management and planning involve discovering whether a task, service, or product can be accomplished in-house or by a vendor. A make-or-buy analysis is an examination method that allows a company to decide which of the mentioned option is better. This analysis is a part of the project’s procurement management plan process which is defined as a procedure of collecting and arranging data about the requirements of a product and analyzing them against other alternatives like a purchase or internal manufacturing.
10+ Make or Buy Analysis Samples
1. Make or Buy Analysis
2. Make or Buy Analysis and Quality Improvement
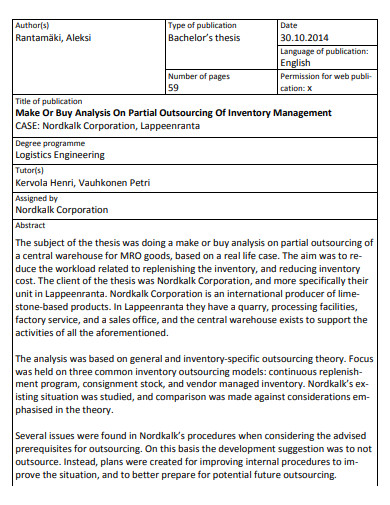
3. Make or Buy Analysis on Partial Outsourcing
4. Sample Make or Buy Analysis
5. Make or Buy Analysis for Cooked Sausage
6. Make or Buy Decision Analysis
7. Simple Make or Buy Analysis
8. Data Make or Buy Analysis
9. Basic Make or Buy Analysis
10. Research Make or Buy Analysis
11. Make or Buy Analysis Planning
What is a Make-or-Buy Analysis?
A make-or-buy analysis is a method used by companies that involve data collection and data analysis to help them decide between creating a product in-house or buying them from an external vendor or supplier. Also known as an outsourcing decision, a make-or-buy decision enables a company to compare the cost and benefits of manufacturing its own product to the cost and benefits of hiring an outside supplier or third party vendor to produce the product. However, even if the company decided to produce its product in-house, it might still need to consider outsourcing some project requirements or components.
How to Write a Make-or-Buy Analysis?
A make-or-buy analysis and decision is the act of utilizing cost-benefit analysis which is a part of a company’s strategic planning to determine whether to manufacture a product or buy its supply from a third party. This process often occurs when a production company has a diminishing capacity, faces issues with its current suppliers, or sees the product demand changing. To achieve an accurate comparison of costs and benefits, project managers will have to analyze the benefits of buying against the benefits of manufacturing the product.
Step 1: Perform Quantitative Analysis
Perform a quantitative analysis to compare the costs that come with each option. This expense refers to the amount paid by a company to purchase a product from a supplier and the cost that the company will pay if they choose to manufacture the product which also includes variable and fixed costs or expenses.
Step 2: Analyze the Qualitative Factors
Analyze the qualitative factors that influence the decision to manufacture the product and the factors that influence the decision to buy the product. If you want to manufacture the product, consider factors such as the quality of your product department and its skills. However, if you choose to purchase from a third-party supplier, consider the quality of their management, dependability, and the quality of their product.
Step 3: Incorporate Qualitative Aspects into Quantitative Aspects
In this step, you have to compare the benefits of the manufactured product against the purchased product. In some cases, a cheaper in-house manufactured product might be lower in grade. And if a company wants to establish a long-term business partnership with a supplier, it might choose to buy the products from them.
Step 4: Make the Final Make-or-Buy Decision
After analyzing and considering both qualitative and quantitative factors, you can now make your final make-or-buy decision. Consider making the decision that would benefit your business in the long run.
FAQs
What are the factors to consider for manufacturing the product in-house?
The major factors to consider for in-house manufacturing of a product are cost concerns, intellectual property concerns, availability of skills and equipment, quality concerns, and unreliable suppliers or vendors.
What are the factors to consider for purchasing the product from a third party?
The major factors you have to consider for purchasing products from an outside supplier are their lack of expertise, cost concerts, lack of manufacturing capacity, quality concerns, low volume requirements, and reverse engineering opportunities.
What are the advantages of a make-or-buy decision?
With a make-or-buy decision, you can determine the lower costs and higher capital investments even if the company decides to manufacture or purchase the product and their source of competitive advantages in which the company considers their external and internal environment.
A make-or-buy analysis is a process in which a company or business gathers and organizes a set of data related to their product requirements and analyzes them against alternatives such as purchasing or internal manufacturing of a certain product. Like outsourcing decisions, a make-or-buy decision compares the cost and benefits of producing in-house goods against the cost and benefits of purchasing them from an outside source.
Related Posts
FREE 10+ Analysis of Alternatives Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Fishbone Root Cause Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 11+ Cost Volume Profit Analysis Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 6+ Corporate Portfolio Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Fault Tree Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Comp Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Fishbone Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Individual Swot Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ 5 Year Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Benefit Costs Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Job Hazard Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Primary Source Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Critical Path Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Competition Analysis Samples in PDF