Option analysis is a methodology based on the premise that changes in the cost and benefit of a prospective IT investment will alter over time. If it doesn’t have any other options, the IT company must stick to the initial decision. The IT organization, on the other hand, can choose to pursue IT expenditures that are later deemed advantageous by providing a future choice option.
10+ Optional Analysis Samples
Simply expressed, options analysis is the process of assessing every alternative path leading to a desired result. Options analysis is an integral aspect of project management since it ensures that leaders have evaluated all options before deciding on the best path for their project. Legislators in the United States, for instance, passed a scheme that would pay incentive money to medical facilities that would abolish paper medical information and substitute them with an electronic health record in an effort to boost value (EHR). There was no middle ground for healthcare professionals. A provider earned the incentive if they embraced the electronic health record; if they did not, their Medicare reimbursements would be subject to a 1% penalty.
1. Impact of the Optional Analysis
2. Optional Features Stress Analysis
The combination of stress analysis, fatigue analysis, and enhanced durability testing yields an indicator of device structural reliability. Finite element analysis (FEA) on a high-performance computer system is commonly used for stress analysis. Through the device production, delivery, and service history, FEA is a numerical approach to compute the optimum stress and strain in the device subject to the stipulated boundary and loading conditions. Materials and manufacturing conditions that are similar to those of completed devices must be used to ascertain the constitutive qualities of the materials.
3. New Optional Analysis
4. Test Optional Analysis
If students provide standardized test scores as part of their application, those results will be factored into the overall evaluation of the application and utilized to determine candidate fit. Some counselors argue that test scores are particularly important now, as grading procedures and GPAs are being revised this spring and maybe this fall. Test-optional policies differ from one school to the next. Some institutions urge students to submit them, while others expect students to provide alternate documentation if a test score is not submitted. Some university programs may have distinct policies than others within the same institution. It’s critical to look into the changed policies at all schools of interest, as they will almost certainly differ.
5. Optional Quicksort Runtime Analysis
How do the worst-case and average-case running times of quicksort differ? Let’s begin by considering the worst-case scenario. Let’s say we’re incredibly unfortunate and the partition sizes aren’t evenly distributed. Consider the case where the partition function always chooses the smallest or largest element in the n-element subarray as the pivot.
6. Optional Testing for Routine Soil Analysis
Collecting the sample is the most important stage in soil testing. It’s critical that you take the measures necessary to obtain a sample; a bad sample could lead to incorrect suggestions. The first step is determining the area that the sample will represent. The physical look, texture, color, slope, drainage, and previous management of the soil should all be consistent across the area. Drawing a map of the land and identifying areas where you will gather samples may be beneficial. Break up any lumps or clods of dirt in the bucket, remove stones, roots, and debris, and thoroughly mix the subsamples.
7. Optional Signal Analysis
The ability to collect and analyze sensitive information delivered by various signals is referred to as signal analysis. This professional captures these signals and analyzes the data using cryptanalysis to decipher the encrypted data.
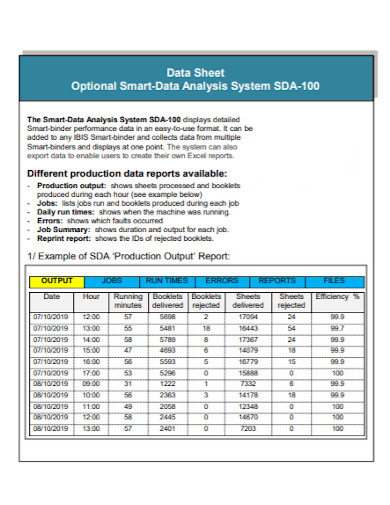
8. Optional Smart Data Analysis
9. Optional Analysis Sample
10. Optional Offer of Analysis
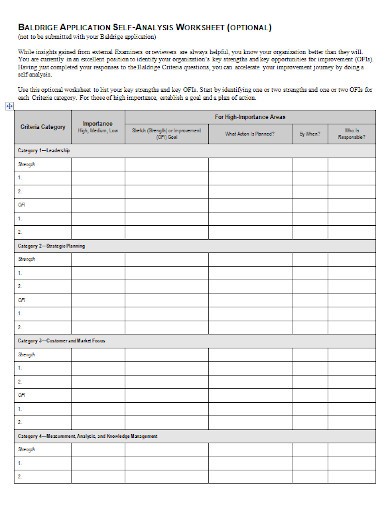
11. Optional Self Analysis Worksheet
FAQs
What is a real options approach?
The real options approach applies monetary alternatives theory to real/non-financial asset options. Options are dependent decisions that allow you to make a decision after a period of uncertainty has passed.
What is real option analysis?
A real option is an economically valued right that a company’s managers have to make or abandon a decision, usually regarding commercial ventures or investment prospects. It’s called “real” since it usually refers to initiatives that include a physical asset (such as machinery, land, and buildings, as well as inventories) rather than a financial instrument.
If you want to see more samples and formats, check out some optional analysis samples and templates provided in the article for your reference.
Related Posts
FREE 10+ Fishbone Root Cause Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 11+ Cost Volume Profit Analysis Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 6+ Corporate Portfolio Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Fault Tree Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Comp Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Fishbone Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Individual Swot Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ 5 Year Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Benefit Costs Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Job Hazard Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Primary Source Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Critical Path Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Competition Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Activity Hazard Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Risk Benefit Analysis Samples in PDF