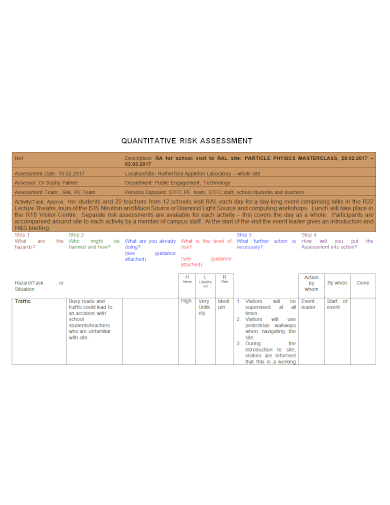
Having an effective risk analysis and management are one of the essentials towards having success especially when it comes to your projects and other endeavors. Depending on the size and scale of the project, it is still necessary to have it delivered on time and within the estimated cost of budget. This would be made impossible if you do not allot some time in identifying, analyzing, categorizing, prioritizing, and gauging with the impacts of the risks. There are two known methodologies commonly used in risk analysis: the qualitative and quantitative. However, there have been a few people who would still struggle to understand how to best employ these methodologies.
10+ Quantitative Risk Assessment Samples
1. Quantitative Method Risk Assessment
2. Environmental Quantitative Risk Assessment
3. Integrating Quantitative Risk Assessment
4. Quantitative Risk Analysis Assessment
5. Quantitative Accident Risk Assessment
6. Quantitative Risk Assessment
7. Quantitative Safety Risk Assessment
8. Quantitative Risk Assessment Methodology
9. Quantitative Development Risk Assessment
10. Quantitative Risk Statement Assessment
11. Sample Quantitative Risk Assessment
All About Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA)
A quantitative risk assessment is a formal type of risk analysis approach that involves a systematic process of quantifying the risks that are being associated with operations of a specific process. It is considered as an essential tool in order to support the understanding of a particular risk especially in relation to employees, environment, company assets, and its reputation. This also aids in making cost effective decisions that would contribute in the management of the entire asset lifecycle.
Some of the objectives contained in a quantitative risk assessment include identifying the hazards that are associated in the facility, determining potential frequencies and consequences, determining the availability of the protection systems, and quantifying risks that are being associated with the facility.
Quantitative risk assessments can also be used in the aspect of health. QRA would usually depend on the type of information coming from various sources including public health surveillance. They are even considered as a consolidated approach for the evaluation of risks when it comes to the industrial systems that are traditionally based on technical failures that can lead to further accident. These scenarios can be a result of the interaction between a series of elements that includes technical to human to organizational domains.
Both the human and organizational factors have a vital role in the development of the situation. Their assessment is crucial to obtain an accurate QRA and effective risk mitigation. QRA has also been identified as something that includes establishment of context, risk identification, performance of risk analysis, and risk evaluation as per the definition from the International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission Standard.
Among the process that are included in achieving the goal is communication, consultation, monitoring, and review activities that should be performed prior to, during, or after the said assessment. QRA also provides authorities and various stakeholders with a basis of implementing awareness about the hazards and risks that exist. Potential measures can be used in order to control or reduce the risk and the effects should also be properly assessed.
Mechanics of a Quantitative Risk Analysis
There are two factors that influence the results for both schedule and cost. The factors refer to uncertainty and identified risks. Uncertainty is the background variability that causes the distinction between the variation and the risks. It is usually caused by the inherent variability of work, error of prediction, and bias in prediction. It is always present in most level of impact. The identified risks are considered as the root causes of variability. They can be measured and mitigated. It is composed of two different types of risk namely the project-specific risks and the systemic risks.
FAQs
What is the difference between a qualitative and quantitative risk analysis?
A qualitative risk analysis is subjective. It focuses more on the process of having to identify a specific risk in order to measure both the likelihood of the occurrence of a specific risk and the impact it may have to the schedule. A quantitative risk analysis is objective. It uses data that is already verified in order to make an analysis of the effects of the risk with regards to the cost overruns, scope creep, resource consumption, and schedule delays.
What are the steps in the risk management process?
It includes identifying the risk, evaluating the risk, and planning and controlling the risk.
What is better when it comes to risk management?
The quantitative approach is considered as the better approach in managing risks as it provides better means of understanding how a particular risk can affect the outcomes of a specific project.
If you want to see more samples and format, check out some of the quantitative risk assessment samples and templates to be guided.
Related Posts
FREE 10+ Event Risk Assessment Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Joint Assessment Samples [ Strategic, Risk, Needs ]
FREE 10+ Teleworker Self-Assessment Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Market Assessment Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Quality Risk Assessment Samples [ Control, Assurance, Management ]
FREE 6+ Immediate Termination of Lease Agreement Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 10+ Qualitative Risk Assessment Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Comprehensive Needs Assessment Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Evaluation Quality Assessment Samples [ Self, Loss, Data ]
FREE 10+ Promotion Assessment Samples [ Health, Self, Employee ]
FREE 10+ Environmental Impact Assessment Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Employee Competency Assessment Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Safety Assessment Samples [ Home, Health, Risk ]
FREE 10+ Change Impact Assessment Samples [ Management, Control, Request ]
FREE 10+ Qualitative Assessment Samples in PDF | DOC