It is strongly recommended that laboratories conduct its own internal quality audit with sufficient frequency to assure the quality of test analyses and make sure that they provide consistent reliable results. An audit will provide the lab with knowledge of how well it follows its own quality programs. Data generated by laboratories are very important in making strategic decisions for all types of projects. It is important that the data released by the laboratory is of the highest possible quality and accuracy, avoid costly resampling and budget overruns. A laboratory audit makes sure that the laboratory not only has quality systems in place, but also fully follows these systems. Follows good laboratory practices, and generates and releases data of maximum quality and integrity.
A laboratory audit checklist is a key element in conducting or planning for a process audit. A good laboratory audit checklist helps you and the laboratory avoid disaster. Laboratory processes are largely important especially in the manufacturing industry. It informs companies and businesses how well a component of a product is and how good it is as a raw material. That is why it’s imperative that laboratories operate in its full maximum capacity. Making sure that the data they are releasing are factual and is reliable overall. Regardless of how confident lab operators are with their own capabilities, there’s no substitute in having a proper approved document that is able to support that claim. Make sure that you yourself are familiar with the document by checking out these laboratory audit checklist samples that we have listed for you down below. Once you’ve gotten yourself acquainted with the document, what it looks like and how it works, feel free to use these samples as guides or even as templates for your own laboratory audit checklist.
10+ Laboratory Audit Checklist Samples
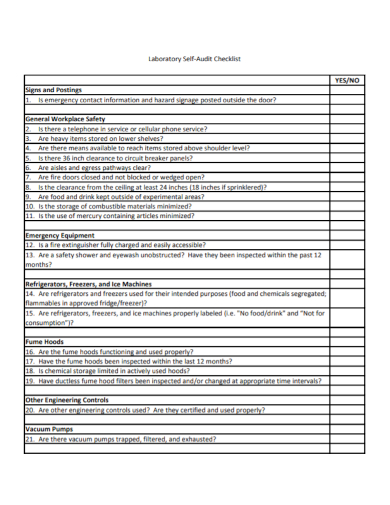
1. Laboratory Self-Audit Checklist
2. Laboratory Health and Safety Audit Checklist
3. Internal Laboratory Audit Checklist
4. Laboratory Safety Hygiene Audit Checklist
5. Laboratory Safety Self-Audit Checklist
6. Laboratory Biosafety Audit Inspection Checklist
7. Environmental Laboratory Safety Audit Checklist
8. Sample Laboratory Audit Checklist
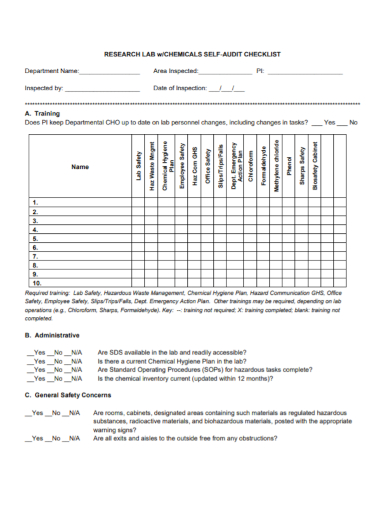
9. Research Laboratory Audit Checklist
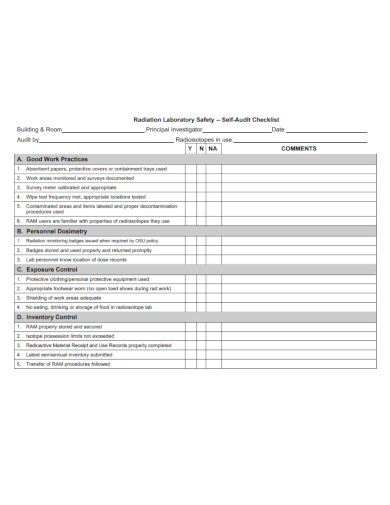
10. Radiation Laboratory Safety Audit Checklist
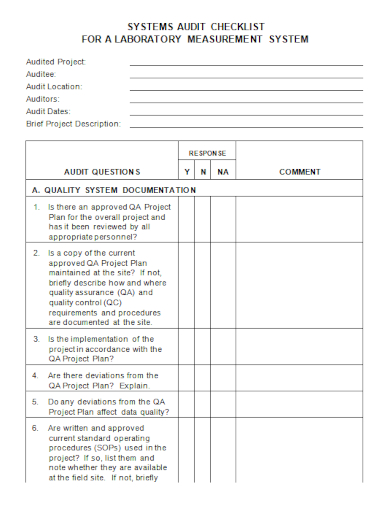
11. Laboratory System Audit Checklist
What Is a Laboratory Audit Checklist?
A laboratory audit checklist is a key element in conducting or planning for an audit process in the laboratory. Considering the ISO standards for workplace and laboratories, a checklist is a tool that consists of questions taken from the quality management requirements, work performance criteria of the process, and the documentation needed for the process that is going to be audited or inspected. Laboratories generally operate on two working principles; either they work in an organization to perform tests for that organization, or they work as a third party to perform tests for various different clients. The inspection is usually conducted by an individual or a group of auditors. Passing an audit provides you and your clients the assurance that the services that you offer is up to the current standards set by the clients, or the ISO standards. The document is vital most especially for establishments such a a laboratory, where quality of data is paramount.
How To Write a Laboratory Audit Checklist
The success of an audit largely depends on the preparation of the laboratory, performance, well documented and insightful reporting, and a productive follow-up. Regardless of the document’s shape or form, it should be able to cover the following components.
- Define the purpose of the audit
Audits are performed to analyze the effectiveness and implementations of the various programs set in the laboratory. These programs are usually designed to maximize the quality of goods or services delivered to the clients. It involves the scope and technical processes to determine the needed resources for the audit. - Define the scope of the audit
The scope of a laboratory audit is defined to its limits or boundaries. Will the scope be focused on corporate or organization? The central laboratory? Or a satellite laboratory? Will analytical methodologies or a specific subset of the laboratory be covered? - Determine the audit team and resources to be used
Determine the skills your team needs to efficiently and effectively handle the scope of the audit. - Identify the authority for the audit
The authority of the audit stems from the company or organization quality assurance manual, the contractor for the analytical services or the request for the third party inspection. - Identify the performance standards to be used
The lab quality system has just as the same amount of shapes, pieces, and names for the pieces as there are authors. Because of this, the audit team must evaluate the client’s quality system against a certain standard. The challenge here is to make sure that whatever the name of the client’s quality system is and how it is described, all the necessary functions are covered and have been properly implemented. - Develop a technical understanding of the processes to be audited
The audit team will be more effective if it has a good grasp of what the target process for the audit is and how it works. Studying the quality manual and implementing certain procedures and historical information from past audits of the laboratory provides the resources needed to focus on the topic and develop better checklists. - Contact the auditee
Make sure that the subject of the audit is informed prior to the actual inspection to be able to ready themselves. The lead auditor needs to make sure it is done or to do it as the situation dictates. The initial contact provides the opportunity to establish a good rapport with the subject. To be able to work out the logistics of the audit and acquire the necessary documents for the audit to come through. - Perform an initial evaluation of lower-tier documents to higher-level requirements
This section is part of the education system of the auditors. The process involves providing much of the focus for the actual audit and data gathering efforts. - Develop written checklists of the data needs
The focus developed in the previous section is documented in this section. Where the audit program is used to cover multiple comparable laboratories, some sections of the checklist are generic. The specific issues need to be examined and listed because the main function of the checklist is to gather enough data.
FAQs
What are the different types of quality audits?
Process audits, product audits, and system audits.
What is the purpose of having an audit in the laboratory?
Audits are used to identify problems in the laboratory in order to improve certain processes and procedures in the lab.
Who hires internal auditors?
Internal auditors are hired by the company, while external auditors are appointed through a shareholder vote. Internal auditors are employed to educate management and staff about how the business and the organization can function better.
Requirements and the overall criteria can vary from one laboratory and client from one another. The overall information is based upon whatever product or service the laboratory might want to focus on. Laboratories always come with their own risks, but having a well written laboratory audit checklist helps alleviate these risks and make sure that whatever services the laboratory might be focused on is accurate and relevant.
Related Posts
FREE 19+ Sample Inventory Checklist
FREE 18+ Inventory Checklist Samples
FREE 18+ Vehicle Inspection Checklist Templates
FREE 15+ Sample Funeral Checklist
FREE 15+ School Checklist Samples
FREE 12+ Observation Checklist Samples
FREE 10+ Retail Cleaning Checklist Samples
FREE 10+ Plumbing Maintenance Checklist Samples
FREE 10+ Sample Risk Assessment Checklist
FREE 10+ Building Inspection Checklist Samples
FREE 15+ HR Checklist Samples
FREE 11+ Retail Store Checklist Samples
FREE 10+ Audit Action Plan Samples
FREE 8+ Housekeeper Checklist Samples
FREE 7+ Equipment Checklist Samples