The world is full of risks and dangers that could potentially ruin a project for your business or an organization. It can bring setbacks and losses to resources or processes that no businesses want to experience. To prepare for those unfortunate events, a risk assessment is done for project managers to be equipped with knowledge on what to do whenever a crisis may unexpectedly strike. This article will guide you on how to make a risk assessment and list down the risks a project may encounter.
10+ Project Planning Risk Assessment Checklist Samples
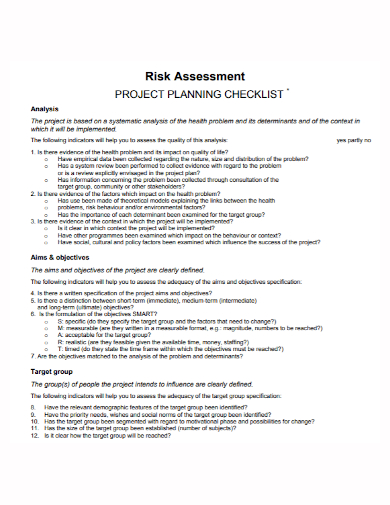
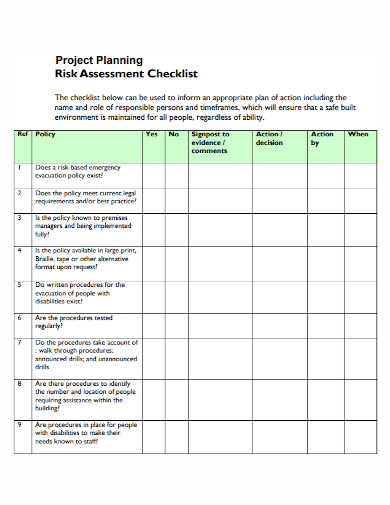
1. Project Planning Risk Assessment Checklist Template
2. Project Planning Audit Risk Assessment Checklist
3. Project Planning Security Risk Assessment Checklist
4. Project Planning Analysis Risk Assessment Checklist
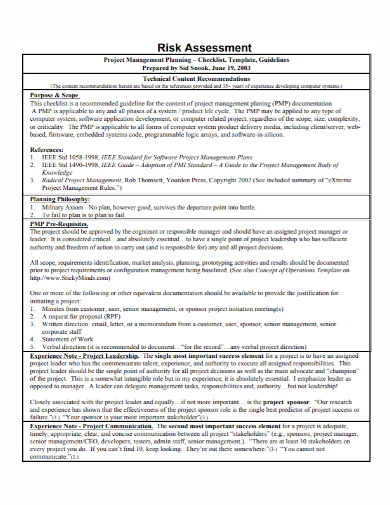
5. Project Management Planning Risk Assessment Checklist
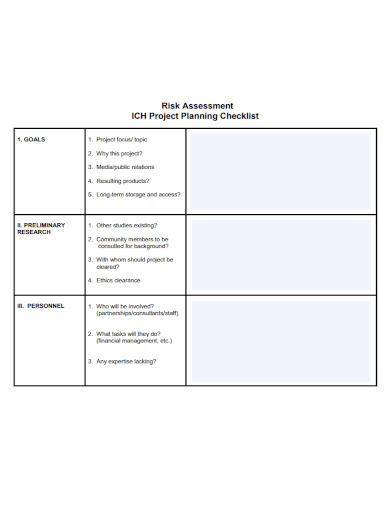
6. Project Goals Planning Risk Assessment Checklist
7. Sample Project Planning Risk Assessment Checklist
8. Standard Project Planning Risk Assessment Checklist
9. Project Planning Review Risk Assessment Checklist
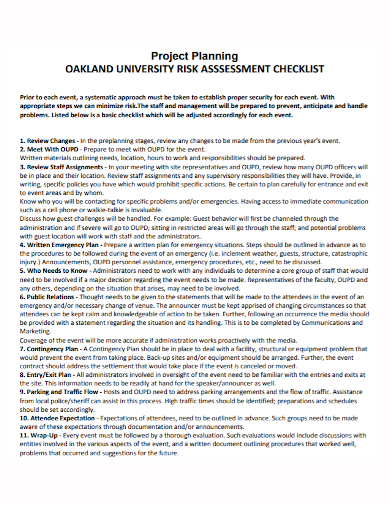
10. Project Planning University Risk Assessment Checklist
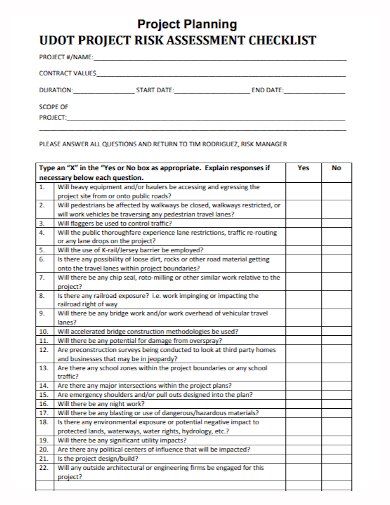
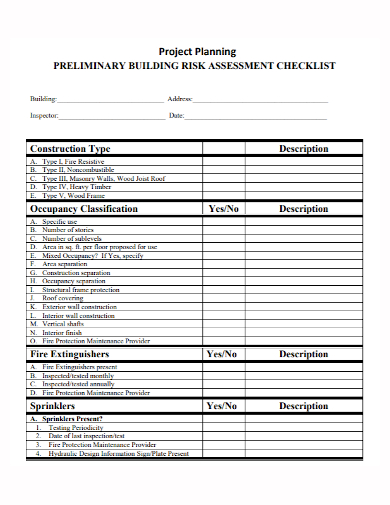
11. Building Project Planning Risk Assessment Checklist
Risks in Project Planning to Include in a Checklist
1. Technology Risk
Project technology can include risks in data security, organization services, compliance, and information security. A new IT program often necessitates new people training and software acquisition. Other technology hazards include service disruptions, which can cause delays and project failure.
2. Communication Risk
When in charge of a project, effective and timely communication is essential. With so many communication tools available, it’s easy to overlook the basics, resulting in data loss, disinformation, and project disruption.
3. Scope Creep Risk
Unauthorized changes to the project scope may result in increased costs for features, products, or services.
4. Cost Risk
A lack of cash or mishandling of funds due to overspending or other constraints jeopardizes the project’s completion. When a project’s cost exceeds budgeted finances, the risk may move to other operations and workers. A reduction in funds may also contribute to a scope risk.
5. Operational Risk
Production or procurement issues might cause a project to delay or fail. Inadequacy or unsuccessful qualitative, quantitative, or tactics could result in direct or indirect loss. Operational risks include:
- IT system vulnerability
- Human and process
6. Health and Safety Risk
Health and safety is a type of risk that can compromise a company’s compliance rules. An organization should have its health and safety standards monitored and evaluated regularly to identify potential risks that can lead the company to losses or fines. The risk can also lead to staff or customers’ health complications where a company’s reputation might be at stake.
7. Skills Resource Risk
Internal staffing is a high-project risk since project operations are sometimes staggered over multiple locations, requiring in-house personnel attendance. Personnel retraining or transfers may be necessary due to staff ineptitude in various project divisions.
8. Performance risk
A project’s perceived performance risk occurs when the anticipated outcome is unlikely. The risk has an impact on the business’s overall success.
9. Market Risk
Market risk occurs when a project’s results do not meet expectations. Competitors may exploit this to weaken and remove the business. Liquidity, credit, and interest rate fluctuations might potentially affect the project’s product sales.
10. External Hazards Risk
A potential risk is an uncontrollable negative event. Terrorism, storms, floods, vandalism, earthquakes, and civil upheaval are examples of such dangers.
How to Do a Project Planning Risk Assessment
1. Identify the Risks
Analyze the risks and consider all possible outcomes before commencing a project. Examine both best and worst-case situations. However, risk management should be immediate. Plan with your client. Diverse viewpoints and levels of experience will help spot dangers.
2. Determine the Probability of the Risks
Examining a danger’s likelihood is an important step in risk assessment. Indicate the importance of each option. So you can focus your resources on the most essential project risks.
3. Determine the Impact of the Risks
The impact varies with the threat. A sick team member won’t necessarily delay your project, but a flu outbreak could. Consider the consequences of each of your mentioned risks. Will it affect delivery? Budget? Identify the risks to your project’s outcome. Those are big dangers. Classify the remaining risks as low to medium.
4. Treat the Risk
This step is known as risk response planning. Plan to treat and reduce the highest risks. Risks can be managed using mitigation, prevention, and response plans.
FAQs
Why is assessing risks in projects important?
Project risk analysis is important because it helps project managers identify the weaknesses, strengths, and possible opportunities during or after completing a project. To effectively analyze risks, one needs to learn and familiarize themselves with the potential problems or “high risk” threats that might negatively affect a scheduled project’s smooth running. It is vital to list all the unexpected events that might disrupt the processes, resources, and technology in an ongoing project to curb or minimize losses.
What are the tools for risk assessment?
- Risk Matrix
- Decision Tree
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- Bowtie Model
Risk management is a continuous process because conditions change. Review, monitor, and track risks periodically throughout your project. Uncertainty plays a major factor in risk management. If you build a process around that uncertainty, you can minimize risk for your project. With less risk, it improves your chances of achieving your project goals. To help you get started creating the checklist, download our free sample templates above to use as your guide!
Related Posts
FREE 18+ Facilitator Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Sheets | PDF
FREE 18+ Complaint Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Sheets | PDF
FREE 18+ Internship Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | PDF
FREE 18+ Statement Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Sheets | PDF
FREE 20+ Voluntary Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Sheets | PDF
FREE 18+ Summary Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Sheets | PDF
FREE 14+ Sponsorship Checklist Samples in MS Word | MS Excel | PDF
FREE 18+ Conference Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Sheets | PDF
FREE 17+ Lesson Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Sheets | PDF
FREE 18+ Progress Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | PDF
FREE 18+ Enrollment Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | PDF
FREE 18+ Graduation Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Sheets | PDF
FREE 15+ Consent Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Sheets | PDF
FREE 18+ Submission Checklist Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | PDF
FREE 18+ Request Checklist Samples in MS Word | MS Excel | PDF