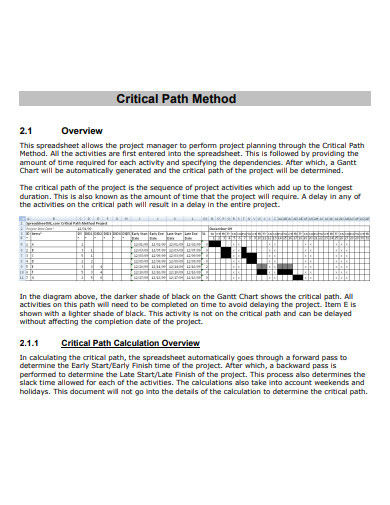
The critical route is the longest sequence of tasks that must be performed to finish a project in project planning. The tasks in the critical route are referred to as critical activities because if they are not completed on time, the entire project would be delayed. The critical path method (CPM) algorithm is used by project managers to determine the shortest time required to finish each task with the least amount of slack. Previously determined by hand, the critical path can now be calculated automatically using project scheduling software with Gantt charts, making the entire CPM technique considerably easier.
10+ Critical Path Samples
The critical path method (CPM) is a strategy for determining schedule flexibility and identifying tasks that are required for project completion. In project management, a critical route is the longest series of operations that must be completed on time in order for the project to be completed. Any delays in crucial activities will cause the entire project to be delayed. Finding the most critical activities in the project timetable, recognizing task dependencies, and estimating task durations are all part of CPM. CPM has grown popular for project planning and work prioritization. It allows you to break down large projects into smaller tasks and acquire a better grasp of how flexible the project is.
1. Critical Path Analysis

2. Agency Critical Path Analysis

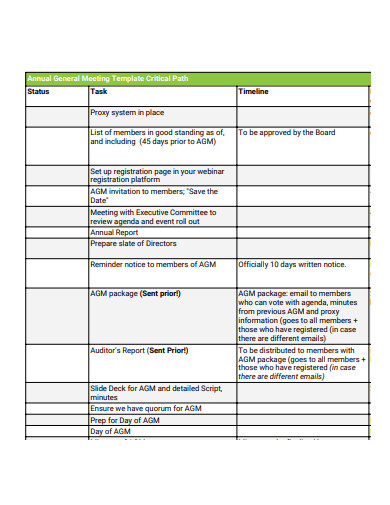
3. General Meeting Critical Path
4. Sample Critical Path
5. Simple Critical Path
6. Basic Critical Path
7. Project Devolopment Critical Path
8. Critical Path Implementation
9. Sample Critical Path Method
10. Critical Path Exercise
11. Printable Critical Path
How to Find Critical Path?
Examining the time of crucial and non-critical jobs can help you find the critical path.
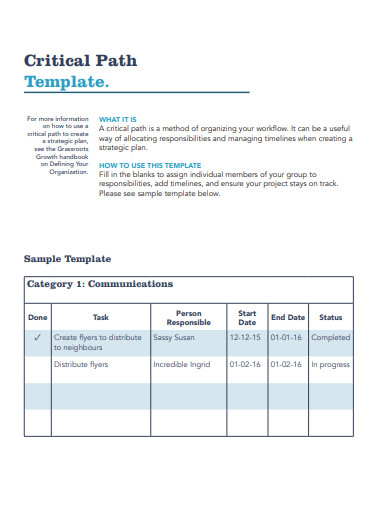
- List activities – List all of the project tasks required to generate the objectives using a work breakdown structure. The work breakdown structure’s list of activities serves as the basis for the rest of the CPM. You can immediately identify task dependencies after you have a high-level notion of everything that has to be done.
- Identify dependencies – Determine the jobs that are interdependent based on your work breakdown structure. This will also assist you in identifying any chores that can be completed concurrently with others. An activity sequence, which will be utilized to define the critical path, is a collection of dependent tasks.
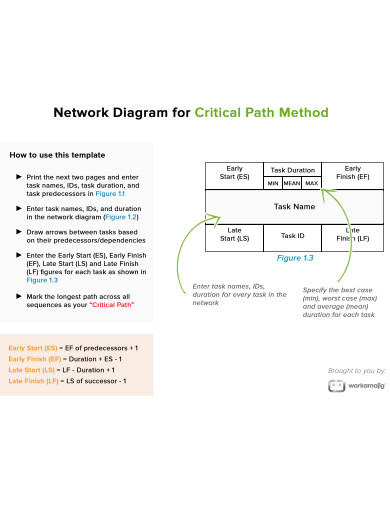
- Create a network diagram – The work breakdown structure is then converted into a network diagram, which is a diagram that shows the sequence of activities. Construct a box for each activity and indicate task dependencies using arrows. You’ll keep adding time-bound components to the schematic until you’ve figured out the overall project timetable.
- Estimate task duration – You must first evaluate the duration of each activity in order to determine the critical path, which is the longest series of critical tasks. The float, or scheduling flexibility, of each activity can then be calculated using the early and late start and end dates.
- Calculate the critical path – You can calculate the critical path manually, but you’ll save time if you use a critical path algorithm. You can create the real project timeline around the critical path once you’ve identified it.
- Calculate the float – The amount of flexibility provided by a task is referred to as float, or slack. It shows how much the work can be postponed without affecting other activities or the project’s completion deadline. Finding the float is helpful in determining how flexible the project is. Float is a resource that should be used to cover project risks or challenges that arise unexpectedly. Critical tasks have a float of zero, indicating that their deadlines are fixed. Non-critical tasks have positive float numbers, which means they can be delayed without compromising the project’s completion deadline. Non-essential tasks may be skipped if time or resources are limited. The float can be calculated using an algorithm or by hand.
FAQs
What is the essential concept behind critical path analysis?
The basic premise of critical path analysis is that certain tasks cannot be started until others have been completed. These tasks must be accomplished in order, with each stage being finished before moving on to the next.
What are the schedule compression techniques?
Fast tracking: Look at the critical path to see what activities can be done at the same time. The overall length will be shortened by running parallel operations.
Crashing: This procedure entails assigning more resources in order to increase activity speed. Before getting more resources, double-check that they are still within the project’s scope and notify the stakeholders of any modifications.
Project management can benefit from CPM, especially when it comes to task planning and resource management. You’ll be able to easily construct timetables and keep track of tasks with the help of project planning tools.
Related Posts
Sample Business Card Templates
Sample Cashier Job Descriptions
Questionnaire Samples
FREE 10+ Sample HR Resource Templates in PDF
FREE 10+ HR Consulting Business Plan Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Pages | PDF
FREE 49+ Sample Job Descriptions in PDF | MS Word
FREE 16+ Nonprofit Budget Samples in PDF | MS Word | Excel | Google Docs | Google Sheets | Numbers | Pages
FREE 13+ Academic Calendar Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
FREE 10+ How to Create an Executive Summary Samples in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
FREE 23+ Sample Event Calendar Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
Company Profile Samples
FREE 10+ Leadership Report Samples [ Development, Training, Camp ]
FREE 24+ Sample Payment Schedules in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Return to Work Action Plan Samples in PDF | DOC
Autobiography Samples & Templates