Graphs are powerful tools that enable us to visually represent and analyze complex relationships and patterns in various fields, such as mathematics, computer science, social sciences, and data analysis strategic plan. From simple bar charts to intricate network graphs, they provide us with a visual language to understand and communicate information efficiently. Bar graphs, line graphs, and pie charts condense large volumes of data into concise and visually appealing formats. Graphs excel at highlighting trend analysis and patterns in business data analysis. Graphs are invaluable tools for discovering insights and opportunities within business data. By visually analyzing graphs, business professionals can spot trends, outliers, and anomalies that can guide them towards new opportunities or potential risk assessment.
30+ Graph Samples
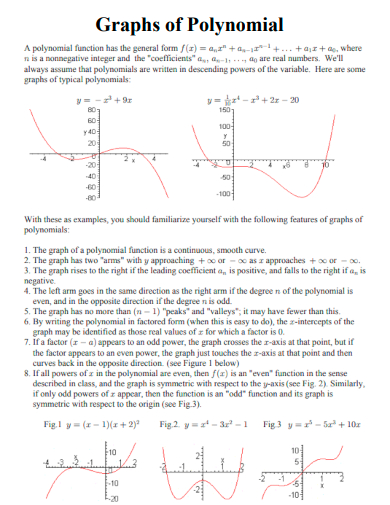
1. Graphs of Polynomial
2. Residual Properties of Graph Products
3. Term Graph Rewriting
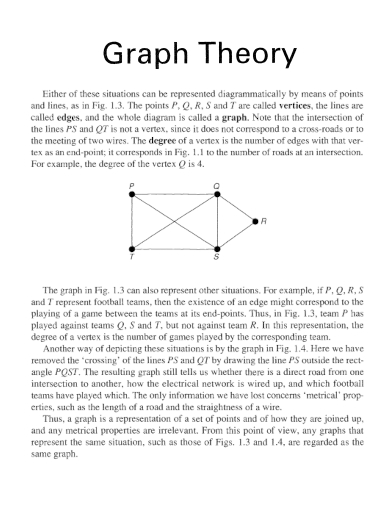
4. Graph Theory
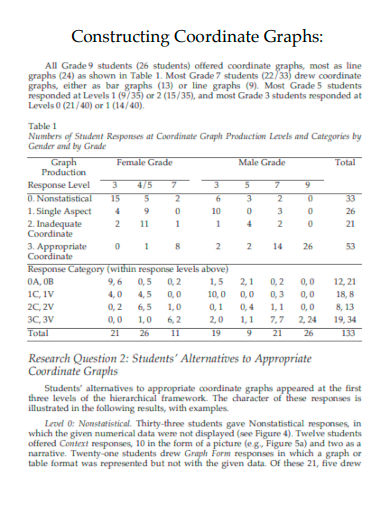
5. Constructing Coordinate Graphs
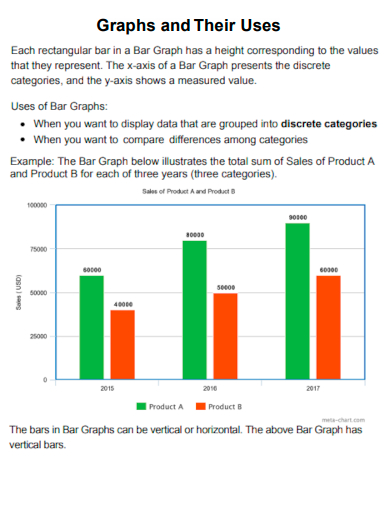
6. Graphs and Their Uses
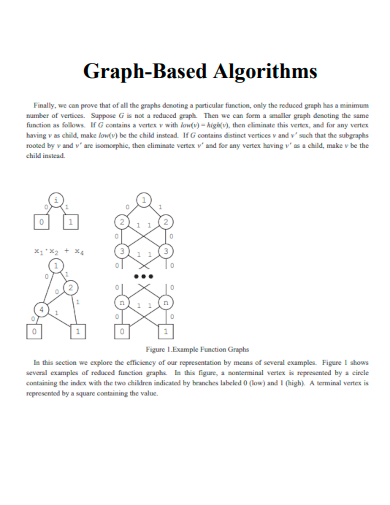
7. Graph-Based Algorithms
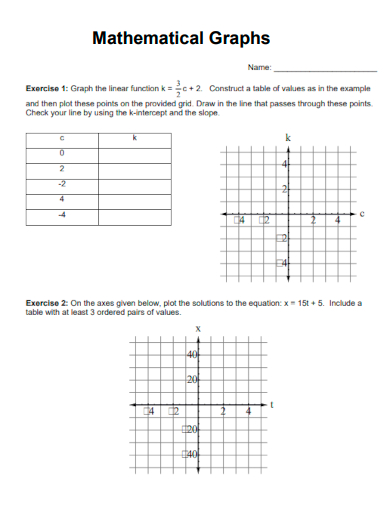
8. Mathematical Graphs
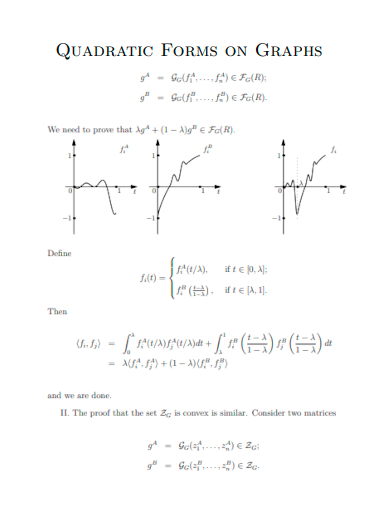
9. Quadratic Forms on Graphs
10. Unconventional Graph
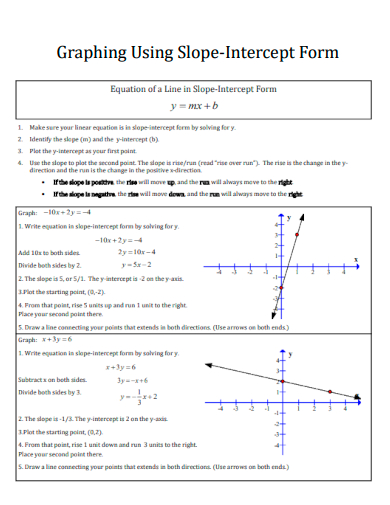
11. Graphing Using Slope-Intercept Form
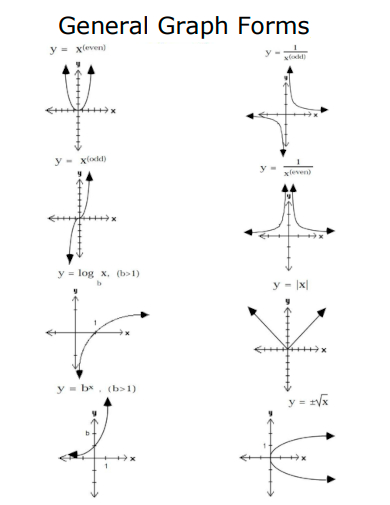
12. General Graph Forms
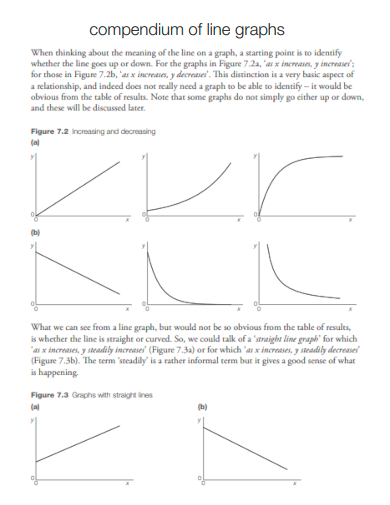
13. Compendium of Line Graphs
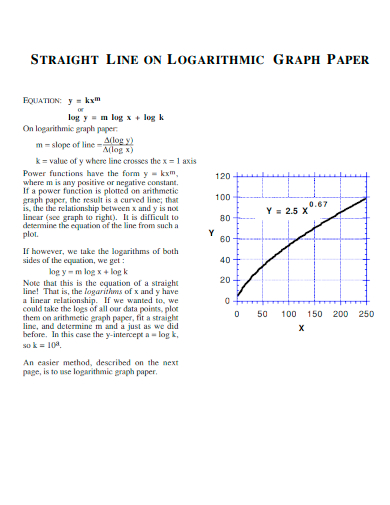
14. Straight Line on Logarithmic Graph Paper
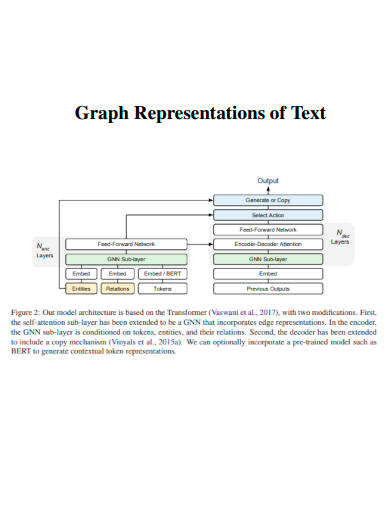
15. Graph Representations of Text
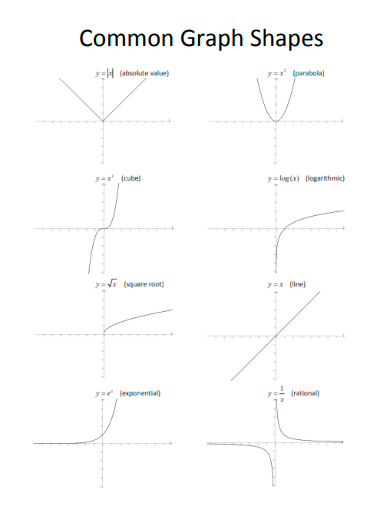
16. Common Graph Shapes
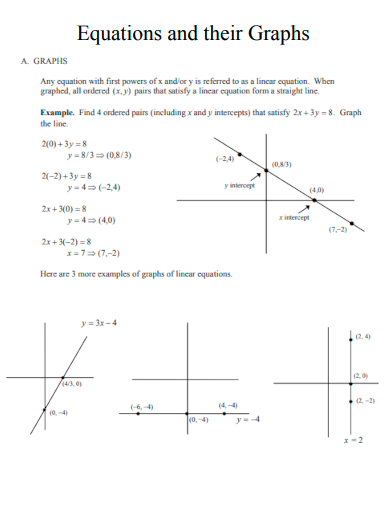
17. Equations and their Graphs
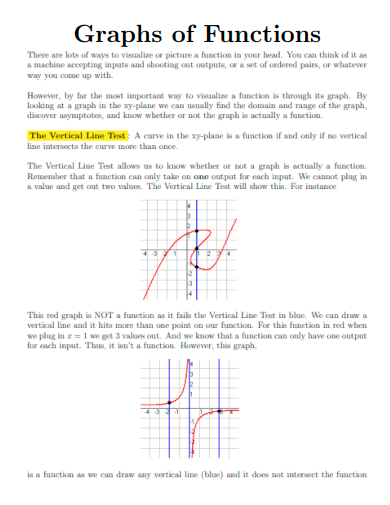
18. Graphs of Functions
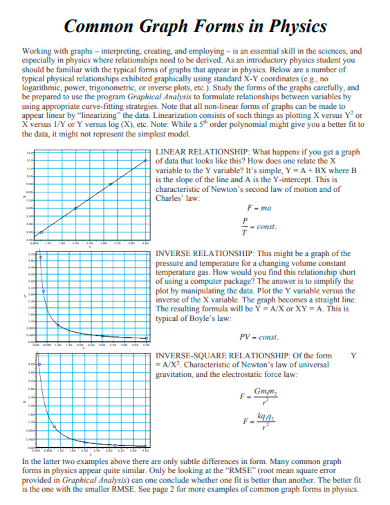
19. Common Graph Forms in Physics
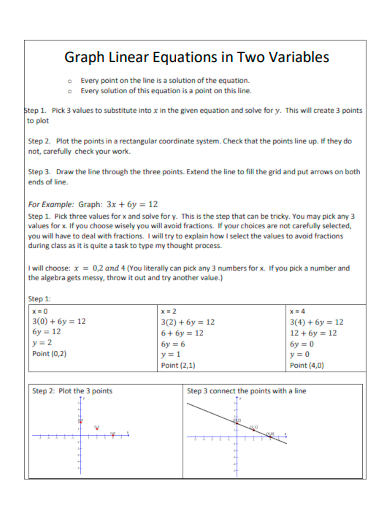
20. Graph Linear Equations in Two Variables
21. Values from a Graph
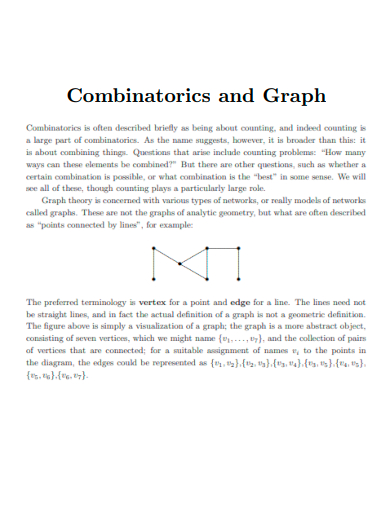
22. Combinatorics and Graph
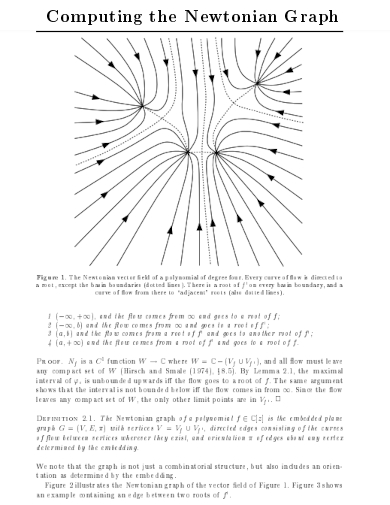
23. Computing the Newtonian Graph
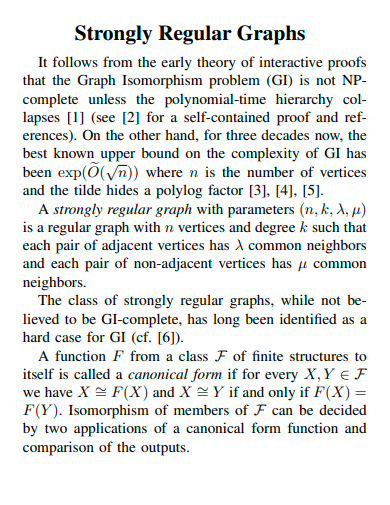
24. Strongly Regular Graphs
25. Feynman-Like Graph
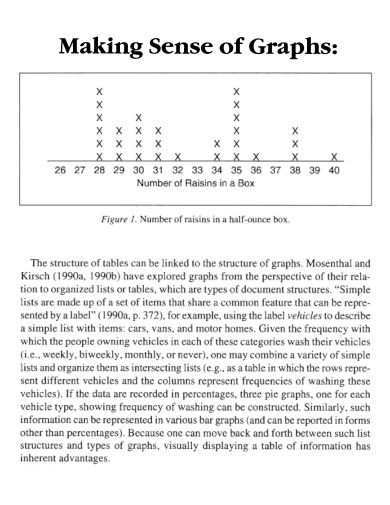
26. Making Sense of Graphs
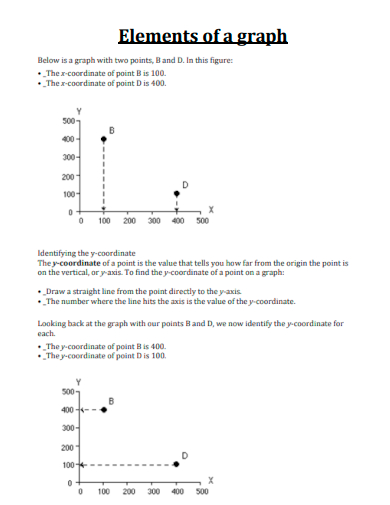
27. Elements of a Graph
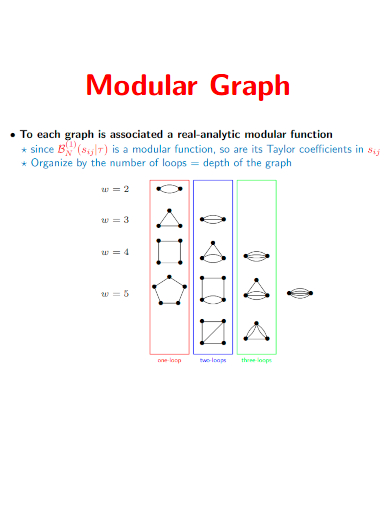
28. Modular Graph
29. Modeling Power of Different Graph
30. Graph Representation Learning
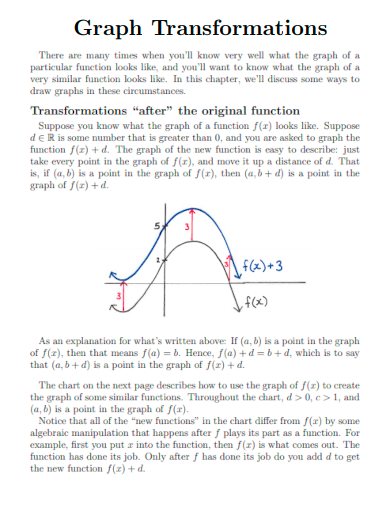
31. Graph Transformations
What is Graph Samples?
A graph, in the context of mathematics and computer science, is a collection of vertices or nodes connected by edges. It is a visual representation of relationships or connections between different elements. A graph consists of two main components: nodes (also called vertices) and edges.
How To Make Graph Samples?
Graphs are excellent tools for communicating and presenting information effectively. They have the power to convey complex ideas in a concise and visually appealing manner, making them accessible to a wide range of audiences. Creating a graph involves a series of steps, depending on the specific context and purpose. Here is a general guide on how to create a graph:
Step 1- Determine the type of graph
First, decide on the type of graph that suits your data and the relationships you want to represent. Common types of graphs include bar graphs, line graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, and network graphs, among others.
Step 2- Gather and organize data
Collect the data you want to visualize and ensure it is organized in a structured format. Depending on the type of graph, you may need data points, categories, labels, and numerical values associated with each data point. There are various software applications and tools available for creating graphs, such as Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, Tableau, Python libraries (Matplotlib, Seaborn), and online graphing tools. Select the one that best suits your needs and familiarity.
Step 3- Enter or import data
Enter your data into the chosen software or import it from a file or database. Ensure that the data is accurately entered, and any necessary formatting or conversions are applied.
Step 4- Select the graph type and layout
Choose the specific graph type that best represents your data and relationships. Consider the variables you want to compare, the level of detail required, and any additional features like axes, legends, and titles. Set up the layout and customize the visual appearance as desired.
How do graphs aid in decision-making?
Graphs assist in decision-making by providing a visual representation of data and relationships. T
What are the advantages of using graphs in presentations or reports?
Using graphs in presentations or progress reports offers several advantages. They help convey complex information concisely and visually, making it easier for the audience to understand and interpret the data.
Can graphs be used for predictive analysis?
Yes, graphs can be used in predictive analysis. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns or trends, graphs can help forecast future outcomes or trends.
In the business world, where data is abundant and decision-making is critical, graphs play a vital role in simplifying complex data, identifying trends, discovering insights, and communicating information effectively. By visually representing data, graphs enable businesses to make sense of large volumes of information, uncover patterns and relationship statement, and extract valuable insights.
Related Posts
FREE 8+ Printable Graph Paper Samples in PDF MS Word
FREE 7+ Sample Hexagonal Graph Paper Templates in PDF MS ...
FREE 6+ Graph Paper Samples in PDF
FREE 6+ Sample Log Graph Paper Templates in PDF MS Word
FREE 6+ Sample Half Inch Graph Paper Templates in PDF MS Word
FREE 6+ Sample Cross Stitch Graph Paper Templates in PDF
FREE 5+ Sample Octagon Graph Paper Templates in PDF
FREE 5+ Sample Semilog Graph Paper Templates in PDF MS Word
FREE 19+ Sample Printable Graph Paper Templates in PDF MS ...
FREE 11+ Sample Dot Plot Examples in MS Word PDF
FREE 9+ 1 Inch Graph Papers in PDF
FREE 9+ Printable Blank Graph Paper Templates in PDF
FREE 6+ Grid Paper Templates in MS Word PDF
FREE 6+ Sample Graph Paper With Axis in PDF
FREE 6+ Printable Grid Paper Samples in PDF PSD