We are lucky to live in a time where sample books and other reading materials are abundant and easily accessible. The reading materials we have available are textbooks, gazettes, newspapers, magazines and journals. While a journal may seem like someone’s diary, it’s actually one of those reading materials that provide detailed and essential information about a topic or subject that is worth knowing. Journal articles are popular in their own way and you are about to find out why.

Download Journal Article Bundle
Journal Article For Students
Title: Navigating the Challenges and Opportunities of Online Learning for Students
Abstract: This article explores the dual facets of online learning, analyzing both the challenges faced by students and the opportunities it presents for educational growth. By examining current trends and student feedback, the paper aims to provide insights into effective strategies for enhancing student engagement and learning outcomes in virtual environments.
Introduction: The shift toward online education has accelerated rapidly, particularly in response to global events such as the COVID-19 pandemic. This transition has prompted an urgent need to assess the impacts of online learning on students across various educational levels.
Challenges of Online Learning: One of the primary challenges in online learning is maintaining student engagement. Without the physical presence of classmates and instructors, students often struggle with isolation and a lack of motivation. Additionally, disparities in access to technology can widen the educational gap among students from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
- Technological Issues: Inconsistent access to reliable internet and digital tools can hinder the learning process, affecting students’ ability to participate in classes and complete assignments.
- Adaptation to Self-Directed Learning: Students are required to manage their time and learning processes more independently than in traditional classroom settings, which can be a significant adjustment.
Opportunities Presented by Online Learning: Despite its challenges, online learning offers substantial opportunities for educational innovation and accessibility. Flexible learning schedules and the ability to access a wide range of resources online are among the key benefits.
- Personalized Learning: Digital platforms allow for a more personalized learning experience, enabling students to learn at their own pace and according to their own learning styles.
- Global Connectivity: Online education breaks geographical barriers, allowing students to connect with peers and experts worldwide, which can enrich the learning experience.
Case Studies and Examples: Several studies highlight how specific strategies have improved engagement and learning outcomes in online settings. For instance, incorporating interactive elements such as real-time quizzes and collaborative projects can significantly enhance participation and learning retention.
Discussion: The effectiveness of online learning varies widely among different student demographics and subjects. It is crucial for educational institutions to continuously adapt and innovate in their online teaching methodologies to address the diverse needs of their students.
- Incorporating Hybrid Models: Combining online and in-person learning can mitigate some of the drawbacks of fully online courses while retaining the flexibility that online education offers.
Conclusion: Online learning is not a one-size-fits-all solution but is a dynamic and evolving educational model. As we continue to navigate its complexities, it is essential to focus on developing inclusive and effective educational practices that address both the challenges and opportunities of digital learning environments.
References:
- Smith, J. (2021). “Engagement in Online Learning: A Comparative Study.” Journal of Online Education.
- Lee, A., & Nguyen, H. (2020). “Access to Technology and the Online Divide.” Educational Technology Review.
- Kapoor, S. (2022). “Hybrid Models of Learning: The Future of Education.” Global Education Journal.
This format provides a structured approach to discussing a topical issue relevant to students, offering a balanced view of the complexities and proposing avenues for future educational strategies.

Journal Article Website
How to Navigate and Use a Journal Article Website Effectively
Navigating a journal article website can be a vital skill for students, researchers, and professionals alike. These websites are treasure troves of academic research and industry insights, offering a range of articles across various disciplines. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to use these resources efficiently.
Understanding the Layout
Journal article websites typically have a structured layout designed to facilitate easy navigation:
- Homepage: This page often features the latest or most popular articles, news about the journal, and links to various sections.
- Search Bar: Located prominently, it allows users to search for articles by keywords, authors, or titles.
- Categories/Archives: These sections help users find articles based on specific subjects or publication dates.
- About: This section provides information about the journal’s scope, editorial board, and submission guidelines.
Effective Searching
To find articles that meet your needs, utilize advanced search features:
- Keywords: Use specific terms related to your research to narrow down results.
- Filters: Many websites allow you to filter results by date, subject area, author, and more.
- Boolean Operators: Use operators like “AND”, “OR”, and “NOT” to refine your searches.
Accessing Articles
Access policies vary by site. Some common methods include:
- Open Access: These articles are freely available to all users.
- Subscription-Based: Access requires a personal or institutional subscription.
- Pay-Per-View: Users can purchase individual articles.
Utilizing Tools and Features
Most journal article websites offer tools to enhance research efficiency:
- Citations: Tools to cite articles correctly in various formats.
- Alerts: Options to receive notifications about new publications in specific areas.
- Reading Lists: Features that allow you to save and organize articles for later reading.
Reading and Interpreting
When reading articles, focus on key sections to assess their relevance and quality:
- Abstract: Provides a summary of the article’s purpose, methodology, results, and conclusion.
- Introduction: Sets up the background and states the research question or hypothesis.
- Methodology: Details how the research was conducted.
- Results/Discussion: Presents the findings and discusses their implications.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the findings and suggests future research directions.
Tips for Effective Use
- Stay Organized: Keep track of your searches and results with tools like bibliographic management software.
- Check References: Use the reference lists of relevant articles to find more related research.
- Stay Updated: Regularly visit journal websites or subscribe to updates to stay informed about the latest research in your field.
By mastering these elements, you can make the most of journal article websites, enhancing your research and keeping abreast of developments in your area of interest. Whether for academic purposes, professional development, or personal interest, these websites are invaluable resources in the digital age.

Academic Journal Articles
Understanding Academic Journal Articles: A Guide for Students and Researchers
Introduction
Academic journal articles are the backbone of scholarly communication, providing a platform for researchers to share findings and contribute to the ongoing dialogue within their respective fields. These articles undergo rigorous peer review and are published in scholarly journals, making them reliable sources of information for students, researchers, and academics.
What are Academic Journal Articles?
Academic journal articles are written by experts in a particular field and are intended to contribute new knowledge or insights to a specific area of research. These articles are characterized by their formal structure, which typically includes an abstract, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and references.
Key Components of an Academic Journal Article
- Abstract: A brief summary of the article, the abstract provides a snapshot of the research questions, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Introduction: This section sets the stage by introducing the research topic, stating the research question, and reviewing the relevant literature.
- Methodology: Here, the author details the procedures and materials used in the study, allowing other researchers to replicate the study if desired.
- Results: The findings of the research are presented in an objective, detailed manner, often accompanied by tables, graphs, and statistical analysis.
- Discussion: The author interprets the results, discusses their implications, and shows how they fit into the larger field of study.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the findings and their implications, discussing the limitations of the study and suggesting areas for further research.
- References: Lists all the sources cited in the article, providing a roadmap to the research’s foundation.
The Importance of Peer Review
Before publication, academic journal articles are subjected to peer review, where other experts in the field assess the validity, significance, and originality of the research. This process ensures the integrity and quality of the research published, making academic articles a trusted source of information.
How to Access Academic Journal Articles
Academic journal articles can be accessed through university libraries, academic research databases like JSTOR, PubMed, and Google Scholar, or through direct subscriptions to academic journals. Many journals require a subscription, but students and faculty can often access these articles for free through their institution’s academic library.
Conclusion
Academic journal articles are essential tools for advancing knowledge and fostering intellectual growth in any academic discipline. They not only disseminate new research findings but also provide a critical foundation for ongoing academic discussions, contributing to the development of new theories and ideas. Understanding how to read, analyze, and derive information from these articles is crucial for any aspiring academic or professional researcher.
Encouragement to Engage
For students and budding researchers, engaging with academic journal articles can be a doorway to deeper understanding and active participation in the field of their interest. Learning how to navigate these articles effectively is an invaluable skill that will enhance their academic and professional pursuits.

Journal Article About Education
Title: Navigating the Shift: The Evolution of Digital Learning in Education
Abstract The landscape of education is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the integration of digital technologies. This article explores the evolution of digital learning, highlighting its impact on teaching methodologies, student engagement, and educational outcomes. By examining various studies and expert opinions, we provide insights into the challenges and opportunities presented by this shift.
Introduction The 21st century has seen a seismic shift in educational practices, primarily due to the advent of digital technologies. From elementary schools to universities, digital tools are being integrated into classrooms at an unprecedented rate. This evolution is not just changing how teachers teach but also how students learn.
The Rise of Digital Learning Digital learning encompasses a range of technologies, including virtual classrooms, online courses, and interactive applications, all designed to enhance educational experiences. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this shift, as institutions worldwide adopted remote learning platforms to continue education amidst lockdowns. This emergency response has provided a vast amount of data and insights into the effectiveness and challenges of online learning.
Impact on Teaching Methodologies Digital tools have introduced new teaching methodologies. Flipped classrooms, where students review lecture content at home and engage in problem-solving during class, and blended learning models, which combine online and face-to-face interactions, are becoming more common. These approaches have shown potential to increase student engagement and facilitate personalized learning experiences.
Student Engagement and Learning Outcomes While digital learning offers flexibility and accessibility, its impact on student engagement varies. Some studies suggest that digital platforms can enhance engagement by providing interactive and tailored learning experiences. However, others point to the potential for decreased motivation due to the lack of physical classroom settings and direct peer interaction.
Challenges of Digital Learning Despite its benefits, digital learning presents several challenges. The digital divide, or the gap between those with or without access to digital technology, remains a significant barrier. Additionally, concerns about screen time, student data privacy, and the effectiveness of remote assessments continue to pose problems for educators and policymakers.
Future Directions Looking forward, the education sector must address these challenges while harnessing the potential of digital learning. There is a need for robust digital infrastructure, effective teacher training programs, and policies that ensure equitable access to technology. Moreover, ongoing research into the pedagogical effectiveness of digital tools will be crucial.
Conclusion Digital learning is reshaping the educational landscape by offering innovative ways to engage students and tailor learning experiences to individual needs. While challenges persist, the future of education will likely continue to be influenced by the evolution of digital technologies. Addressing these challenges head-on will be essential to fully realizing the potential of digital learning.
References (Here, the article would list all the sources of information, studies, and data mentioned throughout the text, formatted according to academic standards.)
This structured approach to discussing digital learning in education allows for a comprehensive examination of its current state and future possibilities, making it a valuable resource for educators, students, and policymakers interested in the ongoing evolution of teaching and learning methodologies.

Browse More Templates On Journal Article
Below are some wonderful journal article samples that you can use as sample reference to help you write relevant and reliable contents to your own journal article.
1. Journal Article Summary Template
2. Scholarly Journal Article in PDF
What Is a Journal Article?
Experts should never stop learning. To feed their need for information, they have what we call a journal. A journal is published periodically throughout the year and contains a collection of articles that are written by experts. You can simply say that journals are written by experts for experts. If you’re not an expert, you can still read journals provided that you understand the topics that are discussed. Journal article writing is a form of professional writing that gives focus on very specific topics. They are also published both in print and online. Journal articles in PDF are just some of the journal article examples that are available online.
- Definition:
- A journal article is a scholarly piece of writing published in an academic journal.
- It represents original research, reviews, or discussions within a specific field of study.
- Components:
- Title and Author(s): Clearly identifies the topic and contributors.
- Abstract: A sample brief summary of the article’s main objectives and findings.
- Introduction: Establishes the context, research question, or hypothesis.
- Literature Review: Surveys existing research related to the topic.
- Methodology: Details the research methods employed.
- Results: Presents the findings of the study.
- Discussion: Analyzes and interprets the results.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the key points and suggests future research.
- Peer Review:
- Articles undergo a rigorous peer-review process where experts in the field evaluate the quality and validity of the research.
- This process ensures the reliability of the information presented.
- Publication Frequency:
- Journals may be published on various sample schedules (monthly, quarterly, etc.).
- The frequency often depends on the specific journal and academic discipline.
- Target Audience:
- Intended for scholars, researchers, and professionals in a particular field.
- Language and content are tailored to the expertise of the target audience.
- Citations and References:
- Articles include citations to acknowledge and give credit to previous research.
- A reference list is provided at the end, allowing readers to explore cited works.
- Formatting and Style:
- Follows a specific formatting style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Adheres to guidelines set by the journal for consistency.
- Access:
- Journal articles can be accessed through academic libraries, online databases, or directly from the journal’s website.
- Some articles may be behind paywalls, requiring a subscription or institutional access.
- Types of Journal Articles:
- Research Articles: Present original research and experiments.
- Review Articles: Summarize and analyze existing research on a specific topic.
- Case Studies: Explore specific instances or examples.
- Opinion or Commentary Pieces: Express the author’s viewpoint on a particular issue.
- Importance:
- Contributes to the scholarly conversation within a discipline.
- Establishes new knowledge, validates existing theories, or challenges current perspectives.
- Impact Factor:
- Some journals are assigned an impact factor, indicating the average number of citations their articles receive.
- Higher impact factors often signify greater influence in the academic community.
- Digital Presence:
- With the rise of online publishing, many journals also maintain a digital presence, facilitating broader access.
Scholarly or Popular: Why Does It Matter?
For most people, magazines are journals and journals are magazines. It seems right, but it feels really wrong to jumble them together and consider them as the same thing. There is a big difference between a magazine and a journal and it’s very important to know which is which. Journal articles are more about scholarly articles that are used as references in many thesis and research papers. It provides an analysis of a particular research topic. When writing a journal article, a specific journal article format is used. Popular magazines or publications on the other hand are not very specific with how their articles are written. The writer is free to use whatever article writing style they prefer. A few examples of popular magazines are National Geographic, Vogue, Time Magazine, and Newsweek.
By knowing the differences between the two types of publications, you’ll be able to choose and use the reference material that is appropriate for the paper your are writing.
3. Reviewing a Journal Article Template
4 Parts of a Journal Article
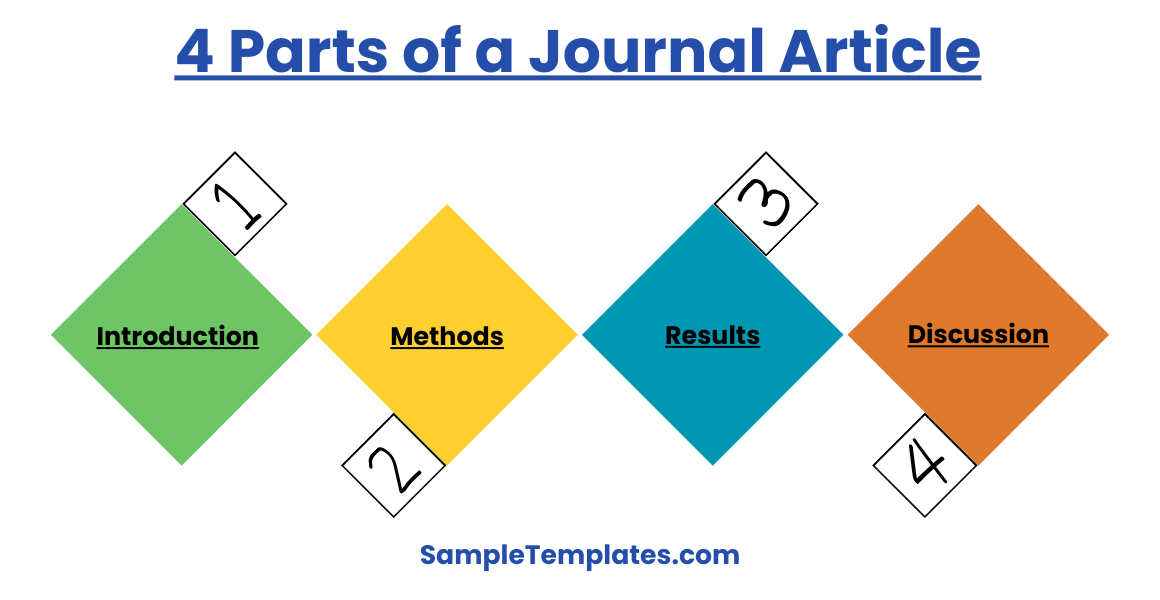
Journal articles, particularly in academic and scientific contexts, typically follow a structured format designed to clearly present research findings and insights. Here are the four main parts of a standard journal article:
- Introduction
- The introduction sets the stage for the research. It outlines the background of the study, the research question, and the problem statement. It often includes a brief literature review to contextualize the study within the existing body of knowledge. The introduction clearly states the purpose and objectives of the research, helping readers understand why the study was conducted and what it aims to achieve.
- Methods (Methodology)
- This section describes how the research was conducted. It details the research design, data collection methods, and analytical techniques used to process and interpret the data. This part is crucial for ensuring the reproducibility of the research; it must be detailed enough that another researcher could replicate the study based on the description provided.
- Results
- The results section presents the findings of the study without interpretation. It often includes statistics, tables, and graphs to display the data clearly. The results should be presented logically and systematically, often in the same order as the methods were described to maintain clarity and coherence.
- Discussion (and Conclusion)
- In the discussion section, the findings are analyzed, and their implications are explored. This part interprets the results, explaining how they answer the research question or address the problem statement outlined in the introduction. The discussion should also relate the findings back to the broader context provided by the literature review, highlighting contributions to the field, limitations of the study, and potential areas for future research. The conclusion may be part of the discussion or a separate section, summarizing the main findings and their practical applications.
These four components are fundamental to the structure of most journal articles, providing a comprehensive and systematic approach to reporting research.
4. Journal Article Reporting Template
5. Evaluating Journal Article Template
How Do you List Journal Articles?
When creating a list of journal articles, it’s crucial to follow a standardized citation style. Common styles include APA (American Psychological Association), MLA (Modern Language Association), and Chicago. Each style has specific guidelines for formatting citations. Below is a general guide based on the APA style:
APA Style Guide for Listing Journal Articles:
1. Author(s):
- List the last name and initials of all authors. Use an ampersand (&) before the last author’s name.
- Example: Smith, J. A., & Doe, M. B.
2. Publication Year:
- Enclose the publication year in parentheses, followed by a period.
- Example: (2022).
3. Title of the Article:
- Capitalize the first word of the title, the first word after a colon, and proper nouns.
- Use sentence case (capitalize only the first word) for the rest of the title.
- End with a period.
- Example: Title of the Article.
4. Title of the Journal:
- Italicize the name of the journal and capitalize all major words.
- End with a comma.
- Example: Journal of Academic Writing,
5. Volume Number:
- Italicize the volume number, followed by a comma.
- Example: 25,
6. Issue Number (if applicable):
- Italicize the issue number in parentheses, without adding a space after the comma.
- Example: (2),
7. Page Range:
- Include the page range of the article, followed by a period.
- Example: 123-145.
6. Professional Journal Article List Template
How to Write an Effective Journal Article and Get It Published
A journal article can be written using an essay writing style. In fact, there are a number of ways to write a journal article. What’s important is you take note of the essential parts or details. You can follow the simple steps provided below.
Step 1: Decide on a topic.
When deciding a topic for your journal article, it is best to choose a topic that you are interested in. It makes writing easier and more enjoyable for you to do. You’re also more knowledgeable about the topic you’re interested in so you can write more about it.
Step 2: Create an outline.
Preparing your outline before actually writing the contents of your journal article helps ensure completeness of your work analysis. It also eases the writing process since you can choose which part to write first and which part to write last.
Step 3: Use the appropriate resources.
Journal articles need to be informative. Informational writing requires you to use reliable sources and only provide facts so as not to mislead your readers. You may also use newspaper article if necessary, but you should be careful on what details to include.
Step 4: Review and make revisions to your work.
Before finalizing the journal article that you have made, make sure that you have all the parts covered from the introduction down to the article summary and conclusion. Also check for any spelling and grammar errors.
Step 5: Publish on print or online.
Decide how you want your work published. Follow the corresponding steps and requirements to have your work successfully published.
7. Sample Checklist for Journal Article Template
8. Journal Article Review in DOC
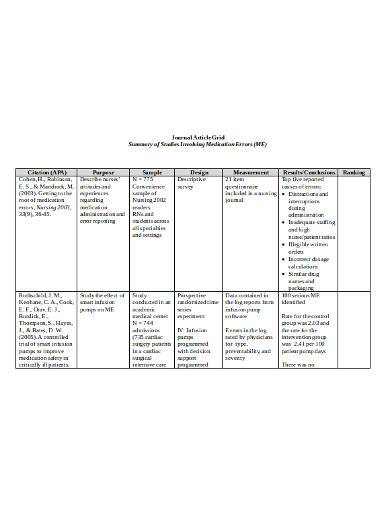
9. Journal Article Grid Template
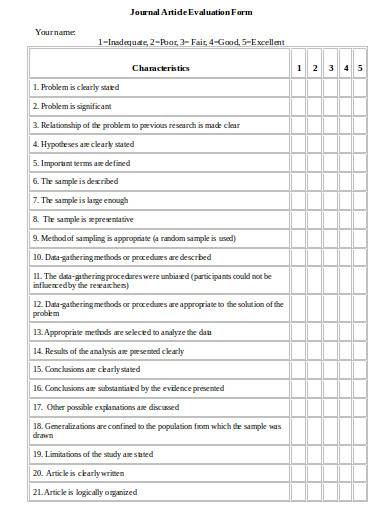
10. Journal Article Evaluation Form Template
How Do I Find a Journal Article?
Finding a journal article involves various methods and sources. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
- Online Databases:
- Utilize academic databases like PubMed, JSTOR, ScienceDirect, or IEEE Xplore.
- Access your institution’s library resources, often providing subscriptions to multiple databases.
- Library Catalogs:
- Check the catalog of your local or university library for physical or electronic journal holdings.
- Explore interlibrary loan services if your library doesn’t have the needed resources.
- Search Engines:
- Use search engines like Google Scholar to locate scholarly articles.
- Adjust settings to link Google Scholar to your library’s collection for full-text access.
- Publisher Websites:
- Visit the websites of publishers known for scholarly journals, such as Elsevier, Springer, or Wiley.
- Some publishers offer open access to certain articles or provide free access after a specific embargo period.
- Institutional Repositories:
- Check if the author or their affiliated institution has uploaded the article to an institutional repository.
- Many universities maintain repositories where researchers share their work openly.
- Citation Tracking:
- Follow references in relevant articles to trace the research backward.
- Use tools like Web of Science or Scopus for citation tracking.
- Specialized Repositories:
- Explore subject-specific repositories for disciplines like arXiv for physics or SSRN for social sciences.
- Some fields have preprint servers where researchers share early versions of their work.
- Professional Organizations:
- Check the sample websites of professional organizations related to your field.
- They may provide access to journals, articles, or resources for their members.
- Social Media and Research Networks:
- Join academic social networks like ResearchGate or Academia.edu.
- Researchers often share their work, and you can request full-text versions.
- Ask Experts:
- Seek recommendations from professors, colleagues, or experts in the field.
- Attend conferences or webinars to connect with researchers and learn about their work.
- Public Libraries:
- Local public libraries may provide access to academic databases or interlibrary loan services.
- Librarians can assist in locating resources based on your needs.
- Government Websites:
- Explore government publications and sample reports on official websites.
- Some government agencies publish research articles related to their work.
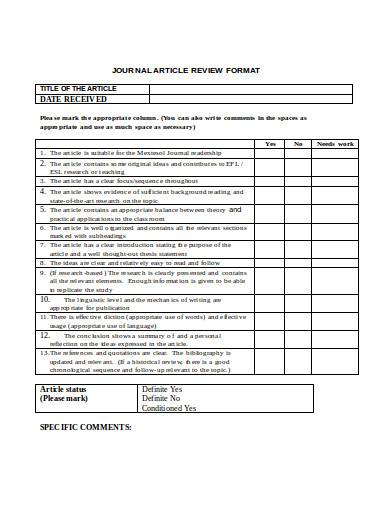
11. Journal Article Review Format Template
12. Journal Article Review Form in DOC
What is the difference between journal and article?
With the samples above, you are sure to write better journal articles. It’s always best to get help from reliable sources because they help you make improvements in your writing style and you learn from them at the same time. The next time you find yourself stuck, just think of the many article summary samples where you can get inspiration from.
FAQS
Is newspaper a journal article?
No, a newspaper article is not the same as a journal article. Newspapers provide news and general information, while journals contain scholarly articles written by experts in specific fields.
What should a journal article include?
A journal article should include a title, abstract, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references, providing detailed insights into the research or topic covered.
What makes a journal article strong
A strong journal article is characterized by clear objectives, rigorous methodology, valid results, insightful discussion, and adherence to ethical standards, contributing valuable knowledge to the field.
How do you identify a good journal article?
A good journal article is identified by its reputable source, well-defined research question, robust methodology, clear presentation of findings, and relevance to the field, contributing valuable insights and knowledge.
What is a journal most commonly used for?
A journal is most commonly used for documenting personal thoughts, experiences, and reflections, serving as a private space for self-expression, goal-setting, and tracking personal or professional development.
In conclusion, a journal article is a valuable tool for personal growth, self-reflection, and process documentation of experiences. It provides a private space to express thoughts, set goals, and track one’s journey.
Related Posts
Weekly Schedule Samples & Templates
Contractual Agreement Samples & Templates
FREE 9+ Amazing Sample Church Bulletin Templates in PSD | PDF
Sample Business Card Templates
Sample Cashier Job Descriptions
Questionnaire Samples
FREE 10+ Sample HR Resource Templates in PDF
FREE 10+ HR Consulting Business Plan Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Pages | PDF
FREE 49+ Sample Job Descriptions in PDF | MS Word
FREE 16+ Nonprofit Budget Samples in PDF | MS Word | Excel | Google Docs | Google Sheets | Numbers | Pages
FREE 13+ Academic Calendar Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
FREE 10+ How to Create an Executive Summary Samples in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
FREE 23+ Sample Event Calendar Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
Company Profile Samples
FREE 10+ Leadership Report Samples [ Development, Training, Camp ]