In a world where safety is paramount, understanding and implementing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is crucial. Whether you’re in a hazardous work environment or simply want to stay protected in your daily life, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge you need. From head to toe, we’ll explore the various types of PPE and provide you with a handy sample checklist to ensure you’re always prepared. Discover the importance of PPE and how it can safeguard you in various situations.
20+ Personal Protective Equipment Samples
1. Personal Protective Equipment Template
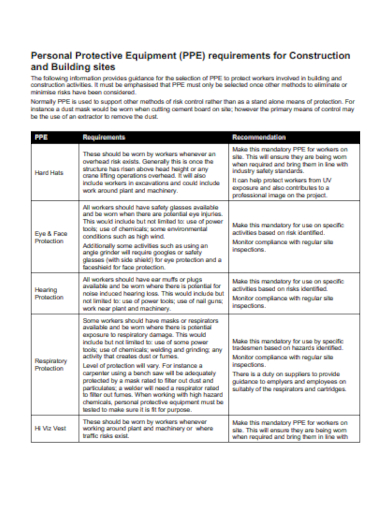
2. Personal Protective Equipment for Construction
3. Laboratory Personal Protective Equipment Assessment
4. Job Safety Personal Protective Equipment
5. Required Personal Protective Equipment for Healthcare
6. Personal Protection Equipment Symbol Template
7. Electrical Work Personal Protection Equipment
What is PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)?
Personal Protective Equipment, commonly referred to as PPE, is a vital component of ensuring safety in various workplaces and environments. It encompasses a wide range of specialized equipment, clothing, and gear designed to protect individuals from various hazards, including physical, chemical, biological, and radiological threats. The primary purpose statement of PPE is to create a barrier between the wearer and potential sources of harm, minimizing the risk of injury or illness.
PPE serves as a crucial defense mechanism in a variety of settings, such as construction sites, healthcare facilities, laboratories, manufacturing plants, and emergency response operations. It plays a pivotal role in safeguarding workers, first responders, and individuals in everyday life from potential dangers. To fully grasp the importance and significance of PPE, it is essential to understand its components and their functions:
Head Protection: Head injuries can be severe and life-threatening. Helmets, hard hats, and bump caps are examples of PPE designed to protect the head from falling objects, electrical hazards, or impacts.
Eye and Face Protection: Safety glasses, goggles, face shields, and full-face respirators shield the eyes and face from chemical splashes, flying debris, and other hazards that can cause eye injuries or facial damage.
Hearing Protection: Earmuffs and earplugs help reduce exposure to high levels of noise, preventing hearing loss and related health issues.
Respiratory Protection: Respirators, masks, and breathing apparatuses are worn to filter out airborne contaminants, such as dust, fumes, gases, or pathogens, safeguarding the respiratory system.
Hand Protection: Gloves, ranging from leather to chemical-resistant options, shield the hands from cuts, burns, chemicals, and infectious materials.
Body Protection: Coveralls, vests, and aprons provide overall protection against physical and chemical hazards, while flame-resistant clothing is crucial for workers in high-heat environments.
Foot Protection: Safety shoes, boots, and steel-toed footwear protect the feet from falling objects, punctures, electrical hazards, and slippery surfaces.
Fall Protection: Harnesses, lanyards, and lifelines are essential for preventing falls from heights, such as in construction or maintenance work.
Skin and Hand Protection: Barrier creams and specialized creams help protect the skin from irritants, chemicals, and potential allergic reactions.
High-Visibility Clothing: Fluorescent clothing with reflective strips is crucial for workers in low-visibility conditions, such as construction sites or roadwork.
Now, let’s delve into the significance of using PPE:
1. Injury Prevention: PPE acts as a shield against injuries, reducing the likelihood of accidents in hazardous environments. It minimizes the impact of accidents when they do occur.
2. Disease Control: In healthcare settings, PPE is vital for preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Items like gloves, masks, and gowns are crucial in protecting both healthcare workers and patients.
3. Legal Compliance: Many regulatory bodies mandate the use of PPE in specific industries to ensure worker safety. Non-compliance can result in legal consequences for employers.
4. Increased Productivity: When workers feel safe and protected, they are more likely to focus on their tasks, leading to increased productivity and reduced absenteeism due to injuries.
5. Peace of Mind: PPE provides peace of mind to individuals working in high-risk environments and their families, knowing that they have taken measures to ensure their safety.
In conclusion, Personal Protective Equipment is a diverse and essential tool for mitigating risks and safeguarding individuals in a wide range of settings. Its use not only protects lives but also contributes to a healthier and more productive workforce. Understanding the various types of PPE and their functions is the first step in ensuring safety and preventing accidents and injuries. Employers and individuals alike should prioritize the correct selection, proper use, and maintenance of PPE to create a safer working and living environment for everyone.
8. Hospital Personal Protective Equipment Planning
9. Personal Protective Equipment for Industry
10. COVID-19 Personal Protective Equipment

cdc.gov
11. Personal Protective Equipment for Chemical
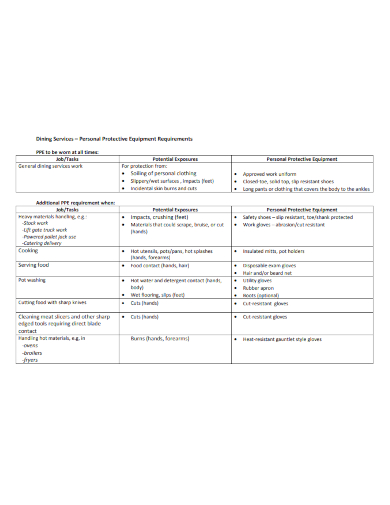
12. Kitchen Personal Protective Equipment
What are the Maintenance Requirements for PPE?
Maintenance of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is critical to ensure its continued effectiveness in protecting individuals from workplace hazards. Proper maintenance not only prolongs the lifespan of PPE but also helps prevent accidents and injuries. Here are the maintenance requirements for various types of PPE:
1. Head Protection (Helmets/Hard Hats):
Regular Inspection: Inspect helmets for cracks, dents, or any signs of damage. Replace if any defects are found.
Cleaning: Wipe the outer shell with a mild detergent and water. Avoid using abrasive cleaners.
Suspension System: Check the suspension system for wear and proper fit. Replace damaged or worn-out parts.
2. Eye and Face Protection (Safety Glasses/Goggles/Face Shields):
Regular Inspection: Examine lenses and frames for scratches, cracks, or damage. Replace damaged components.
Cleaning: Clean lenses with a soft cloth and mild soap or lens cleaner. Avoid abrasive materials that can scratch the lenses.
Adjustment: Ensure a comfortable and secure fit by adjusting headbands or temple arms.
3. Hearing Protection (Earmuffs/Earplugs):
Regular Inspection: Check earmuffs for cracks, broken parts, or signs of wear. Inspect earplugs for cleanliness and integrity.
Cleaning: Wipe earmuffs with a damp cloth and mild detergent. Replace ear cushions if they become damaged.
Earplugs: Dispose of disposable earplugs after single use. Reusable earplugs should be cleaned and stored according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4. Respiratory Protection (Respirators/Masks):
Regular Inspection: Inspect respirators for cracks, damaged straps, or worn-out filters. Replace damaged or worn parts.
Cleaning: Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning and disinfecting respirators. Replace filters or cartridges as recommended.
Storage: Store respirators in a clean, dry place away from direct sunlight and contaminants.
5. Hand Protection (Gloves):
Regular Inspection: Inspect gloves for tears, punctures, or signs of wear. Replace damaged or worn gloves immediately.
Cleaning: Depending on the type of gloves, clean them by hand or machine as per manufacturer instructions.
Storage: Store gloves in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and chemicals.
6. Body Protection (Coveralls/Vests/Aprons):
Regular Inspection: Inspect for tears, rips, or damage to the fabric. Replace damaged clothing.
Cleaning: Follow the care instructions provided by the manufacturer for washing and cleaning.
Repairs: If feasible, repair minor damage promptly to extend the garment’s life.
7. Foot Protection (Safety Shoes/Boots):
Regular Inspection: Inspect for cracks, punctures, or worn-out soles. Replace damaged footwear.
Cleaning: Wipe shoes or boots clean and allow them to dry naturally.
Sole Replacement: Replace worn-out soles as necessary to maintain slip resistance.
8. Fall Protection (Harnesses/Lanyards):
Regular Inspection: Inspect harnesses, lanyards, and connectors for frayed straps, damaged hardware, or signs of wear. Replace damaged components.
Cleaning: Clean harnesses and lanyards according to manufacturer guidelines.
Storage: Store fall protection equipment in a dry, clean area, free from exposure to harsh elements.
9. Skin and Hand Protection (Barrier Creams/Gloves):
Regular Inspection: Check gloves for damage and replace as needed. Ensure creams are within their expiration dates.
Cleaning: Wash hands thoroughly before and after glove use. Barrier creams should be applied as directed.
Regular training and education on PPE maintenance are essential to ensure that workers understand the importance of inspecting and caring for their protective equipment. Employers should establish clear procedures for inspection, maintenance, and replacement of PPE, and employees should be encouraged to report any damaged or malfunctioning equipment promptly. By adhering to these maintenance requirements, workplaces can better protect their personnel and maintain a safe working environment.
13. Nursing Experience Personal Protective Equipment
14. Housekeeping Personal Protective Equipment
15. Workshop Personal Protective Equipment
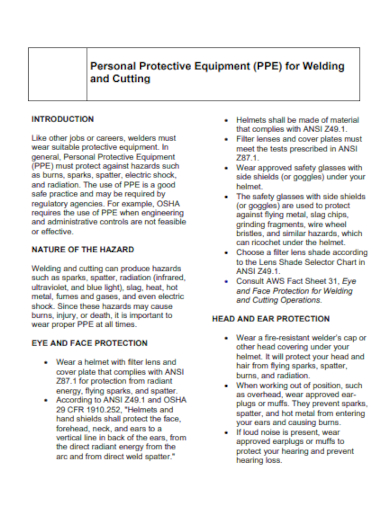
16. Personal Protective Equipment for Welding
17. Engineering Personal Protective Equipment
18. Safety Helmet Personal Protective Equipment
19. Personal Protective Equipment for Workplace
20. Personal Protective Equipment Management Policy
21. Personal Protective Equipment SOP Template
How do I create a PPE program?
Creating a comprehensive Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) program is essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of employees in various work environments. Here are the steps to create an effective PPE program:
1. Assessment of Hazards:
Begin by conducting a thorough hazard assessment of your workplace. Identify all potential risks and hazards that could pose a threat to employee safety. This includes physical, chemical, biological, and ergonomic hazards.
2. Determine PPE Needs:
Based on the hazard assessment, determine the specific PPE required for each task or job role. Consider the type of hazard, its severity, and the likelihood of exposure.
3. Select Appropriate PPE:
Choose PPE that is appropriate for the identified hazards. Ensure that it meets relevant safety standards and regulations. Consult with manufacturers and suppliers for guidance on selecting the right equipment.
4. Employee Training:
Provide comprehensive training to employees on the proper use, care, and limitations of PPE. Training should cover topics such as how to put on and remove PPE, when to use it, and how to maintain it.
5. Establish PPE Policies and Procedures:
Develop written policies and procedures for the use of PPE. These should outline when and where PPE is required, how to obtain it, how to inspect and maintain it, and what to do in case of damage or malfunction.
6. Provide Adequate PPE:
Ensure that there is a sufficient supply of PPE available to all employees who require it. PPE should be properly sized and fitted to each individual.
7. Regular Inspections:
Implement a system for regular inspections of PPE. Employees should inspect their PPE before each use and report any damage or defects immediately. Additionally, conduct periodic formal inspections to ensure compliance.
8. Maintenance and Replacement:
Establish a schedule for maintaining and replacing PPE. Follow manufacturer recommendations for cleaning, repairing, and replacing equipment to ensure it remains effective.
9. Encourage Compliance:
Promote a culture of PPE compliance within the organization. Encourage employees to wear PPE consistently and report any issues or concerns related to PPE.
10. Record Keeping:
Maintain records of PPE inspections, maintenance, and employee training. These records can serve as evidence of compliance with safety regulations.
11. Review and Update:
Periodically review and update the PPE program to reflect changes in workplace hazards, regulations, or advancements in PPE technology. Ensure that the program remains relevant and effective.
12. Continuous Improvement:
Foster a culture of continuous improvement by soliciting feedback from employees regarding the effectiveness of PPE and the program as a whole. Use this feedback to make necessary adjustments.
13. Regulatory Compliance:
Stay informed about relevant safety regulations and standards applicable to your industry. Ensure that your PPE program aligns with these requirements.
14. Supervision and Enforcement:
Supervisors should monitor and enforce PPE usage consistently. Address any non-compliance promptly and educate employees on the importance of adhering to safety protocols.
15. Emergency Response Plan:
Include provisions for PPE in your emergency response plan. Ensure that employees know how to respond in emergencies while wearing their PPE.
Creating a PPE program is a crucial component of workplace safety. It not only helps protect employees from workplace hazards but also demonstrates a commitment to their well-being. By following these steps and maintaining a proactive approach to safety, organizations can create a culture of safety and minimize the risk of accidents and injuries.
Related Posts
FREE 9+ Employer Safety Checklist Samples in PDF DOC
FREE 3+ Workplace Housekeeping Checklist Samples in PDF
FREE 6+ Worksite Inspection Checklist Samples [ Construction ...
FREE 10+ Workshop Risk Assessment Samples [ Vehicle ...
FREE 10+ Construction Method Statement Samples [ Work, Joint ...
FREE 3+ Preschool Incident Report Samples [ Behavior, Childcare ...
FREE 10+ Health and Safety Inspection Checklist Samples ...
FREE 8+ Building Safety Inspection Checklist Samples [ School, Fire ...
FREE 10+ Employee Safety Training Plan Samples in PDF MS ...
FREE 12+ Safety Plan Samples & Templates in PDF MS Word
FREE 10+ Construction Health And Safety Plan Samples [ Phase ...
FREE 5+ Annual Building Inspection Checklist Samples in PDF DOC
FREE 10+ Demolition Scope of Work Samples [ Residential ...
FREE 10+ Safety Observation Report Samples [ Daily, Officer, Site ]
FREE 7+ Industrial Safety Checklist Samples in PDF MS Word