Agricultural projects are ventures that aim to gather agricultural stocks including seeds and seedlings, and the preparation, planting, care, and harvesting, on either owned or leased property of crops and plant-based products to be used as feedstock or for any other industrial projects that is owned or developed by a private company. It works with industry development based on agricultural produce and supports other services for production and processing. This also covers the development of agricultural institutions, managing land ownership issues, credit, education, and training, research, land laws, supervision, infrastructure, and cooperation. Agriculture covers a wide industry since it usually works together with other industries like manufacturing and raw materials list. That is why most project developers conduct more than a few projects to keep this industry innovating to keep up with the ever increasing demand of raw materials, especially plant-based products. And like any large scale project out there, a project proposal has to be initially drafted to secure enough project partners and resources to make sure that the whole project scope is a success.
Project proposals enable project developers to easily and properly present the plans for the whole project and showcase past projects that they have worked on. It also allows them to outline other details such as costs, payments, terms, licenses, and other relevant pieces of information. The goal of the document is to be able to convince potential business partners and project sponsors to join and assist you in your project. A well written project proposal is able to do that and more, secure funding and resources, even grab potential partnerships from other developers working on the same industry. To effectively draft this document, you have to initially make sure that are well versed regarding what the document looks like and how it works. First things first, check out these agricultural project proposal samples we have listed below to get yourself acquainted. Once you are familiar enough, feel free to use these samples as a guide or even as templates for your own agricultural project proposal.

Download Agricultural Project Proposal Bundle
NGO Project Proposal on Agriculture
Project Title: Sustainable Agriculture Development Program
Executive Summary
This proposal outlines the Sustainable Agriculture Development Program aimed at enhancing food security and income for rural communities through sustainable farming practices. Our NGO, GreenGrow Initiative, seeks funding to implement climate-resilient agricultural techniques, provide training to farmers, and establish a community seed bank. The project is designed to impact 500 smallholder farmers over a three-year period in the Midlands region, known for its high poverty rates and underutilized agricultural potential.
Background
The Midlands region faces significant agricultural challenges, including degraded soil, irregular rainfall patterns, and lack of access to modern farming resources. These challenges contribute to persistent poverty and food insecurity among its predominantly farming communities. GreenGrow Initiative proposes a holistic approach to address these issues by promoting sustainable and profitable farming practices.
Project Objectives
- Increase Crop Yield: Enhance the agricultural output of 500 farmers through sustainable farming techniques and improved crop varieties.
- Training and Capacity Building: Conduct workshops on sustainable agriculture, pest management, and resource conservation for local farmers.
- Community Seed Bank Establishment: Create a seed bank to ensure the availability of high-quality seeds resistant to local climate challenges.
- Market Access and Value Addition: Develop partnerships with local markets to ensure farmers can sell their produce at fair prices and explore value addition opportunities.
Project Activities
- Training Sessions: Conduct quarterly training workshops for farmers on innovative farming techniques such as crop rotation, organic farming, and efficient water usage.
- Seed Distribution: Distribute seeds from the community seed bank at the onset of each planting season.
- Field Demonstrations: Implement field demonstration sites as practical, hands-on learning resources for community farmers.
- Market Linkages: Establish agreements with local buyers and co-operatives for the sale of crops produced under the project.
Budget Overview
The total budget for the three-year project is estimated at $250,000. Costs include:
- Personnel: $75,000
- Training materials and workshops: $50,000
- Seeds and farming supplies: $40,000
- Marketing and outreach: $30,000
- Administrative expenses: $55,000
Monitoring and Evaluation
To ensure the success and sustainability of the project, we will implement a comprehensive monitoring and evaluation plan:
- Baseline and Endline Surveys: Conduct surveys at the beginning and end of the project to measure improvements in crop yield and farmer income.
- Regular Field Assessments: Monthly visits by project staff to evaluate the progress of farming activities and provide ongoing support.
- Stakeholder Meetings: Quarterly meetings with community leaders and farmers to discuss project progress and gather feedback.
Sustainability and Future Funding
Post-project, sustainability will be supported by:
- Training farmers to become peer educators, spreading knowledge within the community.
- Reinvesting part of the seed bank’s yearly increase back into the community to ensure its continuity.
- Seeking additional funding and partnerships to scale the project to adjacent regions.
Conclusion
The Sustainable Agriculture Development Program promises to significantly improve the livelihoods of 500 farmers in the Midlands region by increasing agricultural productivity, enhancing food security, and providing stable income sources. Your support can bring this vision to reality, ensuring a sustainable future for these communities.

Mixed Farming Project Proposal
Executive Summary
- Project Title: Sustainable Mixed Farming Initiative
- Project Location: [Location]
- Project Duration: [Start date] to [End date]
- Total Budget: [Amount]
- Project Objective: To establish a sustainable mixed farming system that optimizes the use of land and resources through the integration of crop production and livestock farming.
2. Introduction
- Background Information: Provide context about the farming region, including climate, soil type, and existing agricultural practices.
- Problem Statement: Discuss the challenges currently faced by local farmers, such as low productivity, soil degradation, and limited market access.
- Project Rationale: Explain why mixed farming is a viable solution to the problems identified, emphasizing benefits like improved soil fertility, diversified income sources, and enhanced resilience to market and climatic changes.
3. Project Goals and Objectives
- Main Goal: To improve the economic and environmental sustainability of the local farming community.
- Specific Objectives:
- To integrate crop and livestock production systems to enhance resource efficiency.
- To increase the productivity and profitability of the farm.
- To provide training and support to local farmers on sustainable mixed farming techniques.
- To establish market links for both crop and animal products.
4. Project Methodology
- Land Preparation and Management: Outline the methods for soil preparation, crop rotation plans, and natural resource management.
- Crop and Livestock Integration: Detail the types of crops and livestock to be integrated and the symbiotic relationships between them, such as using manure from livestock to fertilize crops.
- Training and Capacity Building: Describe the training programs for farmers, including workshops on mixed farming techniques, financial management, and market access.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Explain the criteria and methods for monitoring project progress and evaluating the impact on the local farming community.
5. Project Work Plan
- Timeline: Provide a detailed timeline of activities, from initial land preparation to the marketing of farm products.
- Milestones: Set clear milestones for each major phase of the project, such as completing training sessions or achieving target yields.
6. Budget and Funding
- Detailed Budget: Break down the budget into categories such as land preparation, seeds, livestock purchase, training, and marketing.
- Funding Sources: Identify potential funding sources, including grants, loans, and private investments.
- Financial Projections: Offer projections of financial outcomes, showing potential profitability and return on investment.
7. Sustainability and Impact
- Environmental Impact: Discuss the expected environmental benefits, such as enhanced soil fertility and reduced erosion.
- Economic Impact: Analyze the potential economic impact on the local community, including increased incomes and job creation.
- Social Impact: Highlight the social benefits, such as improved food security and community cohesion.
8. Risk Management
- Identification of Risks: List potential risks such as adverse weather conditions, pest outbreaks, and market fluctuations.
- Mitigation Strategies: Describe the strategies to mitigate these risks, including insurance, diversified cropping systems, and establishing emergency funds.
9. Annexes
- Supporting Documents: Include maps, charts, and other relevant documents that support the proposal.
- References: List all sources of information and data used in preparing the proposal.

Youth Agriculture Project Proposal
Project Summary
- Objective: To educate and engage young people in sustainable agriculture practices, fostering environmental stewardship and entrepreneurship.
- Target Group: Youth aged 15-24, particularly in rural areas.
- Expected Outcomes: Increased knowledge of sustainable agriculture, establishment of youth-led agricultural enterprises, enhanced community food security.
Introduction
- Background: Explanation of the current state of youth engagement in agriculture and the potential benefits of increasing their involvement.
- Rationale: Discuss why it is crucial to involve youth in agriculture, focusing on sustainability, the aging farmer population, and economic opportunities.
Project Goals and Objectives
- Main Goal: To empower young individuals with the skills and knowledge to start and sustain agricultural ventures.
- Specific Objectives:
- To train 200 youths in sustainable farming techniques annually.
- To establish a mentorship program linking young farmers with experienced agriculturists.
- To create a small grant fund to support youth-initiated agricultural projects.
Methods and Strategies
- Training Programs: Outline the curriculum for training in organic farming, crop rotation, pest management, and agricultural business practices.
- Mentorship and Support: Details on the mentorship framework and support systems for young farmers.
- Community Engagement: Strategies to involve the community and promote the products of youth-led agricultural initiatives.
Project Timeline
- Phase 1 (Months 1-3): Recruitment and selection of participants.
- Phase 2 (Months 4-12): Intensive training and mentorship program.
- Phase 3 (Months 13-24): Implementation of individual and group projects, with ongoing support and evaluation.
Budget and Funding
- Total Budget: An itemized budget covering training materials, staff salaries, grants for youth projects, and administrative costs.
- Funding Sources: Potential funding sources including government grants, private sponsorships, and partnerships with agricultural businesses.
Monitoring and Evaluation
- Performance Metrics: Criteria for evaluating the success of the project through participant feedback, the number and quality of youth-led enterprises established, and the impact on local food systems.
- Reporting: Regular reporting schedule to stakeholders and funders, including challenges faced and milestones achieved.
Sustainability and Future Funding
- Long-Term Plan: Strategies for ensuring the project’s sustainability, including reinvestment of profits from youth-led enterprises into the program.
- Future Funding Opportunities: Exploration of continuous funding options to expand and enhance the project.
Conclusion
- Summarize the anticipated impact of the project on the youth, community, and local agriculture sector.
- Call to action for support from potential stakeholders and funders.

Project Proposal on Agricultural Cooperatives
Title: Strengthening Agricultural Cooperatives Initiative
Project Summary
- Objective: To establish and support agricultural cooperatives that empower farmers through shared resources, improved market access, and collective bargaining.
- Target Group: Small to medium-sized farmers, including both crop and livestock producers.
- Expected Outcomes: Increased farmer incomes, improved agricultural productivity, and stronger community resilience.
Introduction
- Background: Context on the challenges faced by individual farmers such as market access, cost of inputs, and lack of negotiating power.
- Rationale: Explanation of how cooperative models can address these challenges by pooling resources, sharing knowledge, and consolidating market presence.
Project Goals and Objectives
- Main Goal: To foster sustainable agricultural development through effective cooperative models.
- Specific Objectives:
- To establish 10 new agricultural cooperatives in the target region.
- To provide training and resources to 300 farmers on cooperative management and operations.
- To facilitate access to markets and fair pricing through collective sales and negotiations.
Methods and Strategies
- Formation of Cooperatives: Steps for legally establishing cooperatives, including member recruitment and governance structures.
- Training Programs: Detailed plan for training cooperative members in areas such as financial management, sustainable farming techniques, and market analysis.
- Market Access Strategies: Partnerships with local businesses and government bodies to secure better market access and pricing for cooperative members.
Project Timeline
- Phase 1 (Months 1-6): Community engagement and cooperative formation.
- Phase 2 (Months 7-12): Implementation of training programs and establishment of market connections.
- Phase 3 (Months 13-18): Monitoring and support for cooperative activities, adjustment of strategies based on feedback.
Budget and Funding
- Total Budget: An itemized budget that includes costs for training, legal fees for cooperative formation, marketing, and staff salaries.
- Funding Sources: Identification of potential funding sources such as government agricultural support programs, international development funds, and private sector partnerships.
Monitoring and Evaluation
- Performance Metrics: Evaluation based on the number of cooperatives formed, training sessions held, improvements in market access, and income changes for members.
- Reporting: A plan for regular progress reports to stakeholders, with evaluations of both successes and areas for improvement.
Sustainability and Future Funding
- Long-Term Plan: Strategies for the cooperatives to become self-sustaining, including reinvestment plans and membership fees.
- Future Funding Opportunities: Development of a plan for seeking additional funding and expanding cooperative activities into new regions or sectors.
Conclusion
- Summary of the expected impact of the cooperatives on economic stability and growth for farmers.
- Call to action for support from community leaders, potential funders, and agricultural businesses.

Browse More Templates on Agricultural Project Proposal
1. Agriculture Project Proposal Sample PDF
2. Agriculture Proposal Sample PDF
3. Agriculture Project Proposal Example
Tips On How to Write an Agricultural Project Proposal

- Understand the Needs of Your Audience: Tailor your proposal to the specific needs and concerns of your target audience or funders. Highlight how your project aligns with their values, priorities, and the broader goals of agricultural development.
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define the goals and objectives of your project. Ensure they are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART). This clarity will help stakeholders understand what you sample plan to accomplish and how you will measure success.
- Include Detailed Background Information: Provide a solid background that addresses the existing challenges and opportunities in the agricultural sector relevant to your project. This context will help justify the need for your project and its potential impact.
- Outline a Robust Methodology: Describe the methods and strategies you will use to achieve your project goals. Include information on project activities, timelines, and the resources needed. This demonstrates your project’s feasibility and your preparedness to manage it.
- Engage with Stakeholders: Identify key stakeholders, such as local farmers, agricultural businesses, and government bodies. Outline how you will engage with them to ensure the project meets community needs and gains local support. You can also see more on Research Project Proposal.
- Plan for Sustainability: Show how your project will continue to have a positive impact beyond the initial funding period. This might include plans for scaling up, financial sustainability, or integration into local government programs.
- Include a Comprehensive Budget: Provide a detailed sample budget that includes all potential costs and funding sources. Be transparent about how funds will be used, and ensure that the budget is realistic and justifies the resources required for the project’s success.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Detail your strategy for monitoring the project’s progress and evaluating its outcomes. Include the metrics you will use to assess the project’s impact. This shows funders that you are committed to achieving results and are prepared to adapt if necessary.
4. Example Of Agricultural Extension Project Proposal
5. Agriculture Business Proposal Sample
6. Agricultural Project Proposal Sample
7. Agriculture Project Proposal PDF
Importance of Agriculture Project Proposal
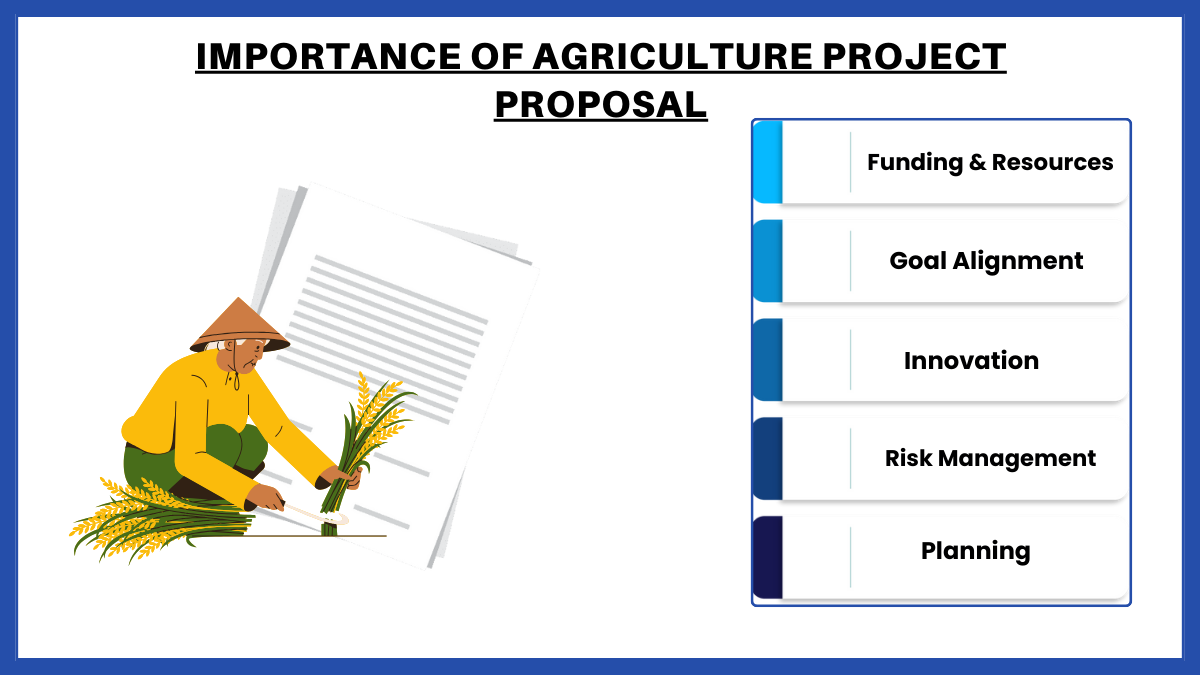
- Securing Funding and Resources: Most agricultural projects require significant financial investment for resources such as seeds, equipment, and labor. A well-crafted proposal is essential to secure funding from governments, NGOs, or private investors. It demonstrates the project’s viability and the efficient use of potential funding.
- Planning and Organization: Writing a proposal forces project planners to thoroughly think through every aspect of the project, from scope and objectives to detailed timelines and budgeting. This preparation helps ensure that the project is well-organized and feasible, reducing the risk of unforeseen issues and financial overruns.
- Goal Alignment and Clarity: Proposals help align the goals of the project with the broader objectives of stakeholders, including community needs, government agricultural policies, and environmental sustainability standards. They ensure every participant and contributor has a clear understanding of the project aims and expected outcomes.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Effective proposals communicate the project’s benefits to various stakeholders, from local farmers to international donors. This communication is essential for building trust and support, encouraging collaboration and buy-in from community members and stakeholders.
- Benchmark for Success: A proposal outlines specific objectives and measurable outcomes, providing benchmarks against which the project’s success can be evaluated. This is crucial for ongoing project management and for reporting to funders and stakeholders.
- Risk Management: Proposals require a detailed analysis of potential risks and their mitigation strategies. This proactive approach helps manage and minimize risks associated with agricultural projects, such as crop failures, market fluctuations, or environmental impacts.
- Innovation and Sustainability: Agriculture project proposals often promote innovative practices and sustainable approaches to farming, which can lead to improved crop yields, reduced environmental impact, and better socio-economic outcomes for communities. You can also see more on Agriculture Business Plan.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many agricultural projects must comply with local, national, and international regulations, especially those that affect land use, environmental protection, and food safety. A detailed proposal helps to outline how these regulations will be adhered to, avoiding legal issues and ensuring ethical practices.
8. Agriculture Project Proposal For Funding
9. Project Proposal Title About Agriculture
10. Example Of Project Proposal In Agricultural Crop Production
11. Agriculture Project Proposal Sample
What Is an Agricultural Project Proposal?
Project proposals are initial documents drafted to initially define both the internal and external aspects of the project that you are working on. It segregates information into different sections like tile, start and end dates of project development, its objectives and goals, requirements, and the descriptor of the project along with the solutions. It functions as a working document between the project developer and the prospective partners or potential investors that might be willing to sponsor additional resources needed. It is drafted and presented prior to the initial developments of the project and because of this, it can also be uses to define the project’s objectives and the requirements needed to green light the development of the project. It also identifies which methods work best to help analyze if the project management is feasible or not. The goal of the document is to convince these key entities to work with you in your project, especially for large scale endeavors like this one. It’s a great way to help secure funding, especially if the project proposal is a success.
How To Write an Agricultural Project Proposal?
Try to see the project proposal as an elaborate marketing device used to marketing project the initial idea of the project and its possible benefits to prospective clients or shareholders and investors. Since we want these people on our side for this project, it is best to draft the document specific to the current nature and scope of the project. Hence, an agricultural project proposal. Keep in mind that the document aims to get these key people on our side. Key entities such as decision makers and investors, to help turn your vision into reality. Let the document speak to the readers, making them realize that working on this project and ensuring its success is in line with what they really want. Listed below are the steps that you need to follow and keep in mind to achieve this.
- Define the problem
Start strong by introducing your problem and why this issue needs to be dealt with. Let your readers see the problem the way you see it. Make sure that your pitch resonates with them by using facts that are supported by real world evidences. Do not exaggerate, keep your statement grounded. You can also see more on Project Cost Proposal. - Present your solution
Present your project as a solution to the problem that you’ve previously identified. Explain why the solution that you’re presenting and the strategies that you’ll be using work better than what was presented before. Prepare yourself for further inquiries and anticipate defending your stand. - Provide deliverables and criteria for success
Give a clear picture of the functions and the attributes of your project deliverables by providing a clear criteria to know if the project is successful or not. It would also be best if you were to provide an estimated span of time in which the project will undergo development and an estimated time when it will be complete. - State your plan
Talk about the project strategies of the project development proposal and the method that you’ll take to achieve your project’s objectives in the given timeframe that you have initially identified. And then explain why these steps are necessary to ensure success. Include what approach you’ll be using in problem solving like whether or not you’ll use a third-party contractor or consultant to assist you. All these details and more should be covered in your project proposal. - Schedule and budget
Break down the project costs and provide as much detail in putting all the details into sections like supplies, tools, and other expenses including indirect costs. A properly laid out financial plan will easily impress the prospective shareholders by showing them that you are well prepared and ready to begin project development. - Summary and conclusion
End your project proposal by tying all the loose ends of your document into a clear and comprehensive conclusion. Circle back to the problem that you’ve initially identified and reiterate the solutions and the strategies that you have covered. Emphasize the more significant parts of your proposal and restate ideas especially ones that you want your readers to remember. - Review and proofread
Before wrapping it all up and submitting it, make sure that you go over it one last time checking if the document is free from typographical and grammatical errors, as well as if it is using the right tone.
Writing a project proposal is no easy task to accomplish, and can be quite daunting for most individuals. It has a lot of weight into it because the fate of the project literally lies upon this document. If the project proposal goes through, then you can presume that you can begin with the development plan in the soonest possible instance.
FAQs
How long should a project proposal be?
The length of a project proposal varies entirely depending on the scale, scope, and nature of the project. However, it is usual for project proposals to be around 4-7 pages long. You can also see more on Agricultural Research.
Which agriculture is most profitable?
Agricultural farm businesses are the most profitable. It includes producing and exporting crops, vegetables, and fruits, and is usually done with minimal investment.
What is a good project proposal?
A good project proposal is clear, well-structured, and persuasive. It should begin with a concise summary, clearly define the project’s goals, objectives, and deliverables, and present a detailed plan with a realistic timeline and budget. The proposal should demonstrate a deep understanding of the problem or opportunity, provide a well-researched methodology, and highlight potential challenges and risks. It should also emphasize the project’s significance and expected impact, align with the needs and interests of stakeholders, and be written in a professional, concise, and compelling manner. A strong project proposal effectively conveys the project’s feasibility, benefits, and aligns with the goals and values of the funding or approving entity.
What is research proposal in agriculture?
A research proposal in agriculture is a detailed plan outlining the objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes of a research project related to agricultural practices, innovations, or issues. It seeks funding or approval for the research.
What are the project topics in agriculture?
Project topics in agriculture can include crop management, soil quality improvement, sustainable farming practices, pest control, livestock management, agricultural technology adoption, and agribusiness development, among others. These topics aim to address agricultural challenges and enhance productivity.
In conclusion, this agricultural project proposal is a comprehensive roadmap to enhance productivity, sustainability, and community welfare. With a focus on innovation and collaboration, we aspire to create a model that not only benefits local farmers but also contributes to broader agricultural advancements. Your support will propel this initiative towards success.
Related Posts
Proposal Samples
Sports Event Proposal Samples
Small Business Proposal Samples
Title Project Proposal Samples [ Community, School, Student ]
FREE 10+ Product Supply Proposal Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 10+ Health Project Proposal Samples [ Public, Mental, Healthcare ]
FREE 11+ Engineering Project Proposal Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 4+ Racing Sponsorship Proposal Samples [ Team, Car, Driver ]
FREE 10+ Nursing Project Proposal Samples [ Community, Health, Clinical ]
FREE 11+ Student Council Proposal Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Facilities Management Proposal Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 8+ Joint Venture Proposal Samples [ Commercial, Real Estate, Construction ]
FREE 10+ Scholarship Proposal Samples [ Project, Grant, Sponsorship ]
FREE 10+ Computer Purchase Proposal Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 10+ Network Project Proposal Samples [ Design, Security, Bank ]