In the ever-evolving world of construction, safety remains a top priority. An integral tool in ensuring a secure work environment is the construction incident report. These documents not only highlight potential hazards but also pave the way for preventative measures. Dive into our comprehensive sample to understand its importance, and get insights on best practices. Embrace a culture of safety, one report at a time.
20+ Construction Incident Report Samples
1. Report Template Bundle

2. Construction Incident Report Template

3. Simple Construction Incident Report Template

4. Blank Construction Incident Report Template
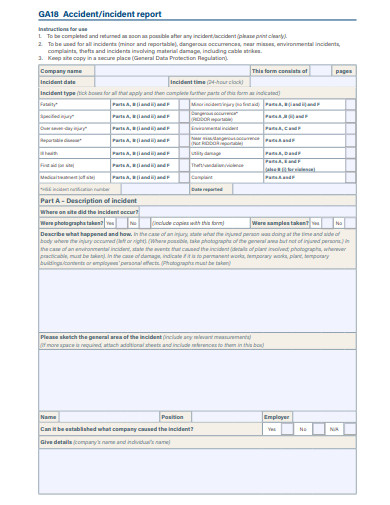
5. Construction Employee Incident Report Template

6. Construction Incident Investigation Report Template

7. Construction Final Incident Report Template

8. Construction Security Incident Report Template

9. Construction Site Incident Report Template

10. Construction Work Incident Report Template

What are the construction incident report samples?
Construction incident report samples are standardized templates that companies use to record, document, and communicate any unwanted events, mishaps, accidents, or injuries that occur on a construction site. These sample reports play a vital role in promoting safety, accountability, and ongoing learning.
Understanding their Purpose
Incident reports in construction aren’t just about documenting an event. They serve multiple purposes:
- Enhancing Safety: By keeping a detailed record of incidents, companies can identify patterns and potential hazards, allowing them to take corrective action.
- Legal Protection: These reports act as evidence in the event of legal disputes, demonstrating due diligence on the part of the construction company.
- Training Resource: Incident reports can be used during training sessions to highlight potential risks and teach workers how to avoid them in the future.
Components of a Typical Report
While the exact format might vary depending on company preferences and regional regulations, most construction incident reports will include:
- Details of the Incident: What happened, where, and when.
- Individuals Involved: Names, roles, and any other relevant details of those who were part of or witnessed the incident.
- Injuries and Damages: Detailed description of any physical injuries to workers or damage to equipment.
- Immediate Actions Taken: What was done immediately after the incident, such as first aid or containment measures.
- Recommendations for Future Prevention: Suggested steps to avoid a repeat of the incident.
The Importance of Accuracy and Timeliness
For an incident report to be effective, it must be accurate and timely. Inaccuracies can lead to improper corrective actions, and delays in reporting can lead to crucial details being forgotten or overlooked.
How do you write a construction incident report sample?
Crafting a well-detailed construction incident report is paramount to ensuring safety, transparency, and learning. A good report is precise, objective, and comprehensive. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing one:
Gather Precise Details
Start by collecting all pertinent details:
- Date and Time: When did the incident occur?
- Location: Where on the construction site did it happen?
- Weather Conditions: Was it rainy, sunny, or windy? This could be relevant, especially if weather played a role in the incident.
Document the Incident
Describe the incident in detail but remain objective. Avoid opinions or assumptions.
- Sequence of Events: Lay out the sequence leading up to the incident. What was happening right before the incident? How did it unfold?
- Immediate Consequences: Were there any injuries or damages? Detail them here.
List the Involved Parties
Mention everyone directly or indirectly involved.
- Personal Details: Name, job title, contact information.
- Role in the Incident: Was the person injured, an eyewitness, or responsible for a certain task when the incident happened?
Detail Immediate Actions Taken
Record the immediate response after the incident.
First Aid: Was any first aid provided? Who administered it?
Notifications: Were any authorities or stakeholders informed?
Include Photographic Evidence
If possible, take photos of the scene. They can provide clarity and support for the written details.
Recommendations and Follow-Up
End your report with preventive measures:
- Suggested Steps: What can be done to prevent such an incident in the future?
- Further Training Needed: Should staff undergo additional training sessions?
Review and Proofread
Before submitting, review the report for clarity and accuracy. Ensure that it is free from grammatical errors and is coherent.
Feedback and Updates
An incident report isn’t just a static document. As investigations continue and more details emerge, update the report. Encourage feedback from team members and experts to make the report as comprehensive as possible.
Remember, the primary aim of a construction incident report is not to allocate blame but to learn from mistakes and implement measures to enhance overall safety on the site.
11. Free Sample Construction Incident Report Template

12. Free Construction Incident Report Template

13. Basic Construction Incident Report Template
14. Construction Work Zone Claim Incident Report Form Template
15. Construction Industry Incident Report Template
16. Construction Status Incident Report Form Template
17. Construction Injured Incident Report Template
18. Formal Construction Incident Report Template
19. Construction Materials Incident Report Template
20. Printable Construction Incident Report Template
21. Major Construction Incident Report Template
What Does an Incident Report Need to Include?
Incident reports play a crucial role in understanding workplace mishaps and preventing future ones. A well-constructed report can be a cornerstone for building a safer and more accountable work environment. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the essential components a typical incident report should encompass:
Incident Details
At the heart of the report are the incident’s specifics:
- Date and Time: Establish when the incident took place. This helps in mapping out the sequence of events and potentially identifying patterns.
- Location: Mention the precise location, whether it’s a specific room, machine, or area within the larger premises.
- Description: Give a detailed, objective account of what happened. Describe the events leading up to the incident and the incident itself.
Parties Involved
It’s crucial to know who was affected or involved:
- Names and Details: List down everyone involved, including their full names, job titles, and contact information.
- Role in the Incident: Detail each person’s role or involvement in the incident. Were they directly affected, witnesses, or first responders?
Nature and Extent of Damages or Injuries
This section dives into the tangible and immediate consequences of the incident:
- Injury Details: Describe any injuries that occurred as a result of the incident, their nature, and severity.
- Property Damage: Outline any damage to property or equipment, with estimations of repair or replacement costs if possible.
Immediate Response
Detail the immediate aftermath of the incident:
- Actions Taken: What steps were undertaken right after the incident? This can include first aid, evacuations, or equipment shutdowns.
- Notifications: Were any external bodies or internal departments informed?
Witness Statements
These provide additional perspectives and can help in understanding the incident better:
- Eyewitness Accounts: Document statements from those who witnessed the incident. It can help in piecing together a clearer picture.
- Supporting Evidence: If witnesses have photos, videos, or any other form of evidence, include them or reference them here.
Recommendations
Looking forward, this section is about learning and prevention:
- Preventive Measures: Based on the incident’s details, suggest steps or measures that can be taken to prevent its recurrence.
- Training or Policy Revisions: Recommend any changes to training programs or organizational policies that could mitigate future risks.
Incident Reporting Mistakes to Avoid
While incident reports are pivotal for safety and compliance, they can sometimes fall short due to common mistakes. Being aware of these pitfalls can ensure your reports are both accurate and actionable.
Subjectivity Over Objectivity
One of the most common mistakes is allowing personal opinions, emotions, or biases to creep into the report. It’s crucial to stick to the facts and present an objective account of the incident.
Omitting Vital Information
Leaving out crucial details can hamper understanding and hinder preventive measures. Ensure all aspects of the incident, even those that might seem minor, are thoroughly documented.
Delay in Reporting
Time is of the essence when it comes to incident reporting. Waiting too long can result in forgotten details or compromised evidence. Sample Reports should be filed as soon as possible after the incident.
Overlooking Witness Accounts
While the immediate parties involved are vital, witnesses can provide invaluable perspectives. Neglecting to include their statements or evidence can result in an incomplete picture of the incident.
Ignoring Follow-Up Actions
A report shouldn’t just end at the incident’s description. Failing to include follow-up actions, be it investigations, corrective measures, or further training, reduces the report’s effectiveness.
Spelling and Grammatical Errors
While the content is king, poor grammar or spelling mistakes can compromise the report’s clarity and professionalism. Always proofread and, if possible, have another pair of eyes review the document.
Avoiding Accountability
An incident report is not about placing blame, but accountability is essential. Avoiding mentioning responsible parties or processes can hinder understanding and corrective action.
Not Updating the Report
As investigations progress and more information becomes available, the report should be updated. Failing to do so means working with potentially outdated or incomplete data.
In conclusion, incident reporting is a vital tool for safety and growth. By ensuring reports are comprehensive, objective, and free from common mistakes, organizations can learn from each incident and build safer, more accountable workplaces.
Related Posts
Sample Book Report Templates
Sample Chemistry Lab Reports
School Accomplishment Report Samples & Templates
Field Report Samples & Templates
Sample Science Project Reports
Business Report Samples & Templates
Survey Reports Samples & Templates
Sample Feasibility Reports
Psychological Assessment Report Samples [ Clinical, Child, Intake ]
Report Format Samples & Templates
Acknowledgement for Internship Report Samples [ Hotel, Hospital, Teaching ]
Field Trip Report Samples [ Agriculture, Educational, Environmental ]
Student Counseling Report Samples
Narrative Accomplishment Report Samples [ Science, Teacher, Reading ]
Sample Acknowledgment Report Templates