The Measurement System Analysis or MSA is a method to experimentally and mathematically determine the amount of variation that a measurement process possesses. These variations can contribute to the overall process variability. The MSA can certify the measurement system used to evaluate a system’s precision, stability, and accuracy. This method is used to assess the quality and quantity of a product and confirms the constancy or measurement variations.
10+ MSA Report Samples
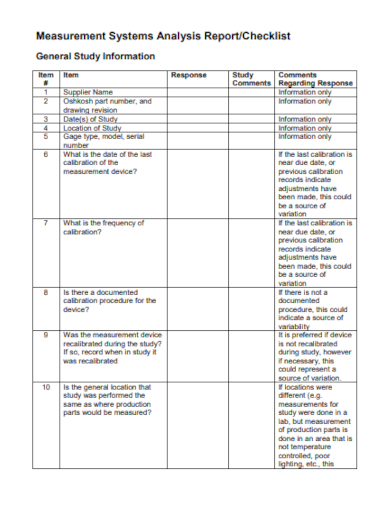
1. MSA Report Checklist
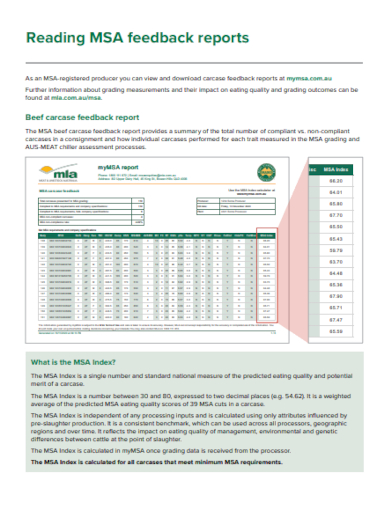
2. MSA Feedback Report
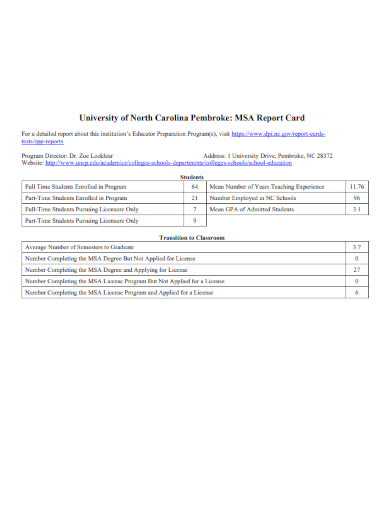
3. MSA Report Card
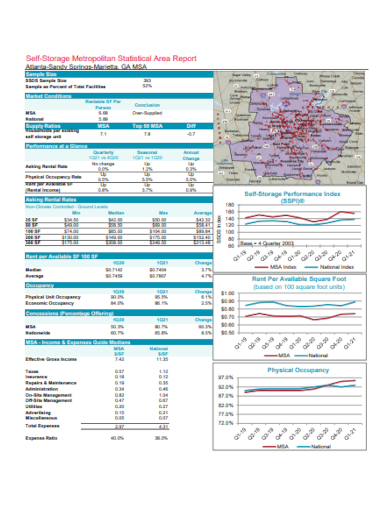
4. Sample MSA Report
5. MSA Safety Annual Report
6. MSA Assessment Report
7. MSA Case Report
8. MSA Coach Incident Report
9. MSA Accreditation Team Report
10. MSA Storage Report
11. MSA Council Activity Report
What is MSA?
The MSA is a formal statistical analysis or study used to determine whether a measurement system, regardless if it is measuring people or devices, is capable of delivering accurate and reliable data management to enable an individual to make more informed and data-driven decisions. It is also a tool used to analyze the existing variations in any type of quality inspection, measurement, and test plan or equipment. With MSA, you can ensure that your data collection process is appropriate and the data you have gathered is accurate and reliable.
How to Create an MSA Report?
One of the most important aspects of MSA is determining whether a measurement system is using the appropriate measurement then followed by the measuring device’s assessment. When often used, measuring tools wear downs or break which makes them less effective. The MSA will also help you in determining whether you need your measuring tools or devices to be replaced, updated, or calibrated.
Step 1: Choose the Type of Data Collection Process
Every manufacturer would want to know if a variation exists in each of their material’s measurements which are called variable data. This data refers to the probable existence of a variable that has measurements that vary on each sample.
Step 2: Determine Sample Collection and Operator
Collect at least 10 random samples of the sheet material as any particular daily production run. After choosing, work with three operators who regularly complete the measurement system process to participate in the analysis. Label each sample with the appropriate lights without the operators knowing before you start the case study.
Step 3: Start the Measurement Process
Each of the operators will measure the 10 sample casings three times which is a total of 30 measurements and record the data as they analyze it. The organizer will rearrange the sample set between each operator to prevent biases.
Step 4: Compare Calculations
After completing three rounds of measurement, the organizer can start the calculation process to determine information about the mean readings for each operator, the standard deviation for each operator, and the difference between each operator’s standard and average deviation.
FAQs
What are the different types of MSA?
The MSA has three main types, including the attribute agreement which refers to the statistical assessment of two or more rater’s consistency of ratings, the variable agreement which helps in evaluating the agreement between two or more agreement systems that produces quantitative data, and the stability which analyzes the consistency of measurement over a certain period of time.
What are the acceptance criteria for MSA?
MSA has three acceptance criteria which include repeatability which refers to the degree that repeated measurements of the same quantity agree, the reproducibility which is the degree that measurements of the same quantity made by different observers agree, and stability which is the degree that measurements of the same quantity made at different times agree.
What are the sources of variation in measurement processes?
In a measurement process, the sources of variation include the process like test method and specification, personnel, tools or equipment such as fixtures and gages, items to be measured, and environmental factors like humidity and temperature.
To determine the amount of variation inside a measurement process, companies or organizations use an experimental and mathematical method called the Measurement System Analysis or MSA. With this method, companies can ensure that they are utilizing the proper data collection method which also ensures the collection of accurate data. With its data analysis, the analysis report from an MSA can deliver the evaluation of a system’s capability, performance, and the measurement of uncertainty about the values measured.
Related Posts
FREE 16+ Sample Sales Reports
FREE 15+ Blank Incident Report Samples
FREE 11+ Variance Analysis Report Samples
FREE 10+ Distribution Report Samples
FREE 10+ Budget Report Samples
FREE 10+ Comprehensive Annual Financial Report Samples
FREE 10+ Sample Case Report
FREE 9+ Market Research Report Samples
FREE 8+ Sample Grant Report Forms
FREE 50+ Sample Reports
FREE 15+ Company and Financial Report Samples
FREE 10+ Consultant Expense Report Samples
FREE 10+ Non-Conformance Report Template Samples
FREE 10+ Accident and Incident Report Samples
FREE 9+ Business Report Samples