Are you writing a literature review? Are you aware of literature review models, types, and elements? Do you need help in writing a literature review? Are you searching Sample Literature Review examples? If our above questions meet your queries, then you have landed to the right destination. Check a list of sample literature review documents below and learn writing custom literature reviews. Our sample literature review documents contain examples, guidelines, and sample brief information about literature review writing and research paper.

Download Literature Review Bundle
Literature Review Format
Introduction
- Background: Briefly introduce the topic and its significance.
- Objectives: State the purpose of the literature review.
- Scope: Define the scope and boundaries of the review.
2. Thematic or Chronological Organization
- Theme 1/Time Period 1:
- Summary of Key Studies: Summarize the main findings of relevant studies.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of these studies.
- Gaps and Limitations: Identify gaps in the research and limitations of the studies reviewed.
- Theme 2/Time Period 2:
- Summary of Key Studies: Summarize the main findings of relevant studies.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of these studies.
- Gaps and Limitations: Identify gaps in the research and limitations of the studies reviewed.
- Theme 3/Time Period 3:
- Summary of Key Studies: Summarize the main findings of relevant studies.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of these studies.
- Gaps and Limitations: Identify gaps in the research and limitations of the studies reviewed.
3. Methodological Approaches
- Comparison of Methods: Compare the different methodologies used in the studies reviewed.
- Evaluation of Approaches: Discuss the effectiveness and limitations of these methodologies.
4. Discussion
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the findings from the reviewed studies, highlighting common themes and patterns.
- Research Gaps: Identify and discuss the gaps in the current literature.
- Implications: Explain the implications of these gaps for future research.
5. Conclusion
- Summary of Key Points: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review.
- Relevance to Current Study: Explain how the literature review informs and supports your current research project.
- Future Directions: Suggest areas for future research based on the identified gaps and limitations.
6. References
- Citations: List all the references cited in the literature review in the appropriate format (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).

Literature Review For Grant Proposal
Introduction
The proposed research aims to address critical gaps in the understanding of [specific topic or problem]. This literature review provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies key gaps, and demonstrates the necessity of the proposed study.
Background
The research topic of [specific topic] has garnered significant attention due to its implications for [related field or societal impact]. [Key terms and concepts] are central to this field of study and will be used throughout this review to provide clarity and focus.
Historical Development
Research on [specific topic] has evolved over the past decades, beginning with foundational work by [early researchers]. In the early [years], studies primarily focused on [early research focus]. For example, [specific study] by [author(s)] demonstrated [key finding]. This work laid the groundwork for subsequent research by establishing [important concept or methodology].
Current State of Knowledge
In recent years, the focus of research has shifted towards [current research focus]. Numerous studies have explored [specific aspects], with notable contributions from [author(s)] such as [study 1] and [study 2]. These studies have advanced our understanding by [specific advancements], yet significant gaps remain.
Trends and Methodologies
The current literature reveals several trends. Firstly, there has been a growing emphasis on [trend 1], as highlighted by [author(s)]. Secondly, methodological advancements have played a crucial role in [methodological trend], as evidenced by [study 3]. These trends underscore the dynamic nature of research in this field.
Gaps in the Literature
Despite these advancements, several key gaps persist. For instance, [gap 1] has not been adequately addressed. Studies such as [study 4] have highlighted the need for [specific research need], but comprehensive investigations are lacking. Additionally, [gap 2] remains understudied, as noted by [author(s)] in [study 5]. Addressing these gaps is essential for advancing both theoretical understanding and practical applications.
Importance of Proposed Research
The proposed research aims to fill these critical gaps by [specific aims of the proposed research]. By leveraging [methodology or approach], this study will provide new insights into [specific aspect], thus contributing to [broader impact]. This research is poised to [specific contributions], thereby advancing the field and informing future studies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while significant progress has been made in the field of [specific topic], important gaps remain. The proposed research is designed to address these gaps, offering the potential to significantly advance our understanding and application of [specific topic]. This literature review underscores the necessity and relevance of the proposed study, highlighting its potential impact on the field.

Literature Review For Students
Introduction
The integration of technology in education has been a subject of extensive research and debate over the past few decades. This literature review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge regarding the impact of technology on student learning. It will explore the benefits, challenges, and the effectiveness of various technological tools and approaches in enhancing educational outcomes.
Background
Technological advancements have revolutionized many sectors, including education. From the introduction of personal computers to the proliferation of mobile devices and online learning platforms, technology has fundamentally altered how students access information and interact with educational content. Understanding the implications of these changes is crucial for educators, policymakers, and researchers.
Historical Development
The use of technology in education dates back to the early 20th century with the introduction of educational films and radio programs. However, the most significant developments have occurred in the last few decades. According to Saettler (1990), the introduction of personal computers in the 1980s marked the beginning of a new era in educational technology. Subsequent innovations, such as the internet and mobile devices, have further transformed the educational landscape (Cuban, 2001).
Current State of Knowledge
Recent research has focused on the diverse ways in which technology can enhance student learning. For instance, a study by Clark and Mayer (2016) found that multimedia learning tools can significantly improve student understanding and retention of information. Similarly, Mayer (2009) demonstrated that well-designed educational software could facilitate more effective learning by providing interactive and engaging content.
Benefits of Technology in Education
One of the primary benefits of technology in education is its ability to provide personalized learning experiences. According to Pane et al. (2015), adaptive learning technologies can tailor educational content to meet the individual needs of students, thereby improving learning outcomes. Additionally, technology can facilitate greater access to educational resources, especially for students in remote or underserved areas (Kozma, 2003).
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential benefits, the integration of technology in education also presents several challenges. For example, Warschauer (2003) highlighted the issue of the digital divide, where students from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may lack access to necessary technological tools. Moreover, some educators may not be adequately trained to effectively incorporate technology into their teaching practices (Ertmer & Ottenbreit-Leftwich, 2010).
Effectiveness of Specific Technologies
Various studies have examined the effectiveness of specific technologies in enhancing student learning. For instance, the use of interactive whiteboards has been shown to increase student engagement and motivation (Smith et al., 2005). Similarly, online learning platforms, such as MOOCs, have the potential to democratize education by providing free access to high-quality courses (Yuan & Powell, 2013).
Gaps in the Literature
While there is substantial research on the impact of technology on student learning, several gaps remain. For instance, more studies are needed to examine the long-term effects of technology on learning outcomes. Additionally, there is a need for research that explores how different student populations, such as those with special needs, are affected by educational technologies (Selwyn, 2011).
Conclusion
In conclusion, the literature suggests that technology can have a positive impact on student learning by providing personalized and engaging educational experiences. However, challenges such as the digital divide and the need for effective teacher training must be addressed to fully realize the potential of educational technology. Future research should focus on addressing these gaps and exploring the long-term effects of technology on education.

Literature Review For Action Research
Introduction
This literature review explores the existing research on [specific topic or problem], focusing on studies that inform the proposed action research. Action research seeks to address practical issues through iterative cycles of planning, action, observation, and reflection. This review identifies key themes, methodologies, and gaps in the literature, demonstrating the need for the proposed research.
Background
The context for this action research is [specific context or setting], where [brief description of the problem or situation]. Key terms such as [key terms] are defined to provide clarity and ensure a common understanding throughout this review.
Historical Development
The study of [specific topic] has evolved significantly over time. Early research by [author(s)] in the [years] focused on [initial focus]. For instance, [specific study] by [author(s)] demonstrated [key finding]. This foundational work established [important concept], which has since been expanded upon by subsequent research.
Current State of Knowledge
Recent research on [specific topic] has concentrated on [current research focus]. Notable studies include [study 1] by [author(s)], which found [key finding], and [study 2] by [author(s)], which explored [specific aspect]. These studies have provided valuable insights into [specific area], yet they also highlight the complexity and multifaceted nature of [specific topic].
Trends and Methodologies
Several trends have emerged in the literature. Firstly, there has been an increased emphasis on [trend 1], as seen in studies such as [study 3]. Secondly, innovative methodologies like [methodology] have been employed to address [specific issue], with [study 4] serving as a prime example. These trends reflect the evolving nature of research in this field and the diverse approaches being used.
Gaps in the Literature
Despite these advancements, several gaps remain. One significant gap is [gap 1], which has been noted by [author(s)] in [study 5]. Additionally, [gap 2] remains understudied, as highlighted by [author(s)] in [study 6]. Addressing these gaps is crucial for developing a more comprehensive understanding of [specific topic] and for informing effective action in practical settings.
Relevance to Action Research
Action research is uniquely suited to address the identified gaps due to its iterative and participatory nature. The proposed study aims to [specific aims], building on the work of [author(s)] and employing [methodology]. This approach will enable a thorough investigation of [specific aspect] and facilitate the development of practical solutions that are directly applicable to [specific context or setting].
Importance of Proposed Research
The proposed action research is designed to address the identified gaps and contribute to both theoretical and practical knowledge. By focusing on [specific aims], this study will provide actionable insights and foster positive change in [specific context]. The iterative cycles of action research will ensure that findings are continually refined and adapted to meet the needs of stakeholders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while significant progress has been made in understanding [specific topic], important gaps remain. The proposed action research addresses these gaps through a systematic and participatory approach, offering the potential to advance both theory and practice. This literature review underscores the necessity and relevance of the proposed study, highlighting its potential impact on the field and its practical applications.

Browse More Templates On Literature Review
Literature Review Template
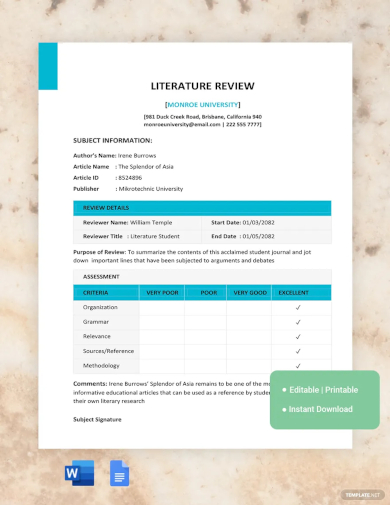
Sample Research Paper Literature Review Template

Details
File Format
Size: 816 KB
DownloadThis PDF is a sample literature review system example written in APA MLA format. Read and analyze this sample document for writing a literature review. Check the basic literature review format and elements used in the example. This PDF contains a red highlighter mark that describes the key points.
How To Write a Literature Review?
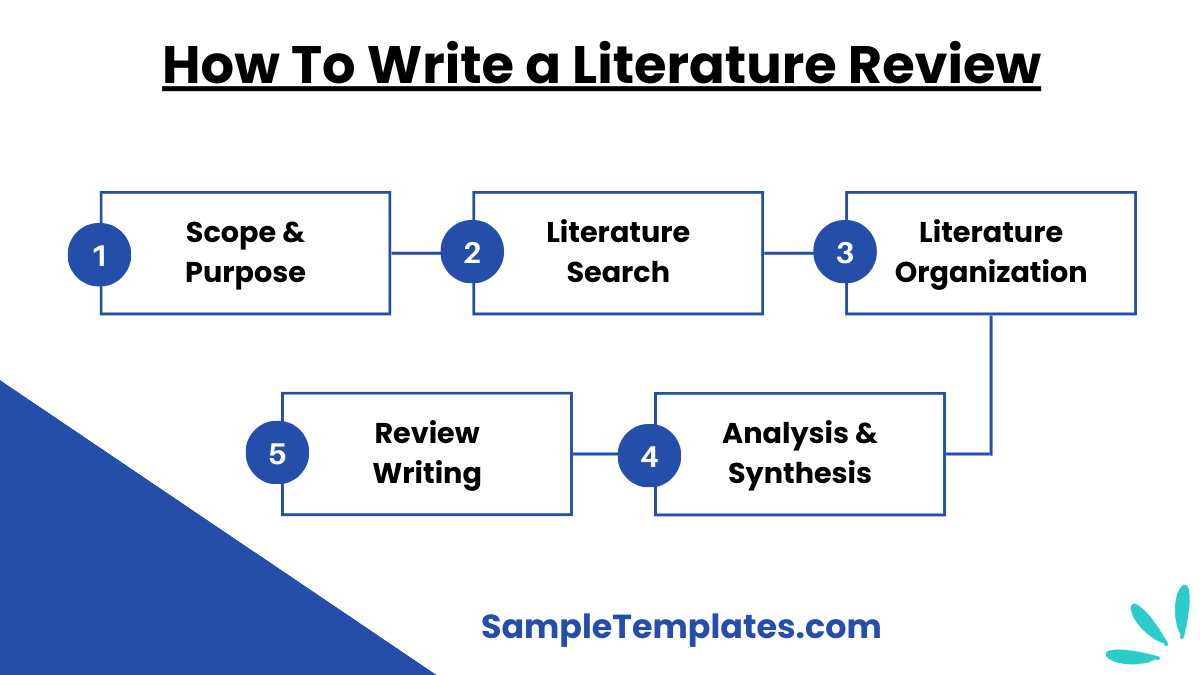
1. Define the Scope and Purpose
- Clarify the Focus: Determine the specific topic, research question, or problem your sample literature review will address.
- Establish Objectives: Clearly state the purpose of the review, such as summarizing current knowledge, identifying gaps, or providing a theoretical framework for your research.
2. Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Search
- Identify Sources: Use databases, academic journals, books, and other scholarly sources to find relevant literature.
- Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria: Set criteria for selecting studies, such as publication date, relevance, and quality, to ensure a focused and relevant review.
3. Organize the Literature
- Thematic Organization: Group the literature into themes, trends, or categories that align with your research focus.
- Chronological or Methodological Order: Alternatively, organize studies by chronological order to show the development over time, or by methodology to compare different research approaches.
4. Analyze and Synthesize Findings
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, and contributions of each study. Highlight key findings and their implications for your research.
- Synthesis: Integrate the literature, drawing connections between studies to identify patterns, trends, and gaps. Show how the literature collectively informs your research question.
5. Write the Review
- Introduction: Introduce the topic, scope, and purpose of the review. Provide context and define key terms.
- Body: Present the organized literature, summarizing and synthesizing findings in a coherent manner. Use subheadings for clarity.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main findings, highlight gaps in the literature, and discuss the significance of your review. Explain how your research will address the identified gaps and contribute to the field.
By following these steps, you can create a structured and informative literature review that effectively supports your research. You can also see more on Book Review.
Thesis Literature Review Template

Details
File Format
Size: 506 KB
DownloadThis PDF contains a flow chart for writing a custom literature review. Download the PDF and learn the best way of writing an effective thesis literature review for engaging and impressing the readers. Also, you get a guide on literature review strategies through sample examples.
Formal Literature Review Template

Details
File Format
Size: 113 KB
DownloadIf you do not know anything about literature review writing, then you should download this PDF. It contains a briefing note on literature review including definition, elements, strategies, and its types. Once you read it, you will not need a second document or guidance for writing a custom literature review.
What are the 5 Rules For Writing a Literature Review?
1. Be Selective
- Focus on Relevance: Choose studies that are directly relevant to your research question or topic. Avoid including irrelevant or marginally related studies to keep your review concise and focused.
- Quality over Quantity: Prioritize high-quality, peer-reviewed sources and seminal works that have significantly contributed to the field.
2. Be Comprehensive
- Cover Key Works: Ensure you include major studies, key theories, and important findings related to your topic.
- Use a Range of Sources: Draw from a variety of sources, including books, journal articles, and credible online resources, to provide a well-rounded perspective.
3. Be Critical
- Evaluate Sources: Critically assess the methodology, findings, and contributions of each study. Identify strengths, weaknesses, and biases.
- Compare and Contrast: Highlight agreements, disagreements, and debates within the literature to show the complexity of the topic.
4. Be Organized
- Structure Logically: Organize your review in a coherent manner, whether thematically, chronologically, or methodologically. Use subheadings to guide the reader.
- Synthesize Information: Integrate findings from different studies to provide a comprehensive overview, rather than just summarizing each study individually.
5. Be Clear and Concise
- Use Clear Language: Write clearly and concisely, avoiding jargon and overly complex sentences. Ensure your review is accessible to a broad audience.
- Maintain Focus: Stay focused on your research question or objectives, and avoid unnecessary details that do not contribute to your review’s purpose.
By adhering to these rules, you can create an effective and insightful literature review that supports your research objectives and contributes to the scholarly conversation on your topic.
Nursing Literature Review Example

Details
File Format
Size: 181 KB
DownloadSample Essay Literature Review Template

Details
File Format
Size: 23 KB
DownloadTips For Writing a Literature Review

Certainly! Here are some practical tips to help you write an effective literature review:
1. Start Early
- Time Management: Begin your literature review well in advance to allow sufficient time for reading, analyzing, and organizing the literature.
2. Define a Clear Scope
- Narrow Focus: Clearly define the scope of your review to keep it focused and manageable. Specify the topics, time periods, and types of studies you will include.
3. Use Reliable Sources
- Credible Databases: Utilize reputable academic databases like PubMed, Google Scholar, JSTOR, and others to find high-quality, peer-reviewed articles.
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Prioritize primary research articles over secondary sources, such as reviews or meta-analyses, to ensure originality.
4. Take Detailed Notes
- Summarize Key Points: While reading, summarize key points, methodologies, findings, and relevance to your research.
- Organize Notes: Keep your notes organized by themes, methodologies, or chronological order to streamline the writing process.
5. Develop a Logical Structure
- Organize Thematically or Chronologically: Choose a structure that best suits your topic. Thematic organization groups studies by topics, while chronological organization shows the development over time.
- Use Subheadings: Use subheadings to break the text into clear sections and guide the reader through your review.
6. Synthesize, Don’t Summarize
- Integrate Findings: Synthesize information from multiple studies to highlight trends, patterns, and gaps in the literature.
- Critical Analysis: Provide a critical analysis of the literature, discussing strengths, weaknesses, and contributions to the field.
7. Maintain a Critical Perspective
- Evaluate Sources: Critically evaluate the quality, methodology, and reliability of the sources. Discuss any biases or limitations.
- Identify Gaps: Point out gaps in the existing literature and how your research will address them.
8. Use a Consistent Citation Style
- Follow Guidelines: Use the citation style recommended by your institution or publication, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago.
- Organize References: Keep track of all sources and organize them properly in your reference list.
9. Write Clearly and Concisely
- Avoid Jargon: Use clear, straightforward language and avoid unnecessary jargon.
- Be Concise: Be concise and focus on the most relevant points to keep your review engaging and informative.
10. Revise and Proofread
- Multiple Drafts: Write multiple drafts and revise for clarity, coherence, and logical flow.
- Proofread: Carefully proofread your final draft to correct any grammatical errors and ensure consistency in style and formatting.
By following these tips, you can write a well-organized, insightful, and impactful literature review that effectively supports your research objectives. You can also see more on Primary Research Report.
Psychology Literature Review Outline Template

Details
File Format
Size: 30 KB
DownloadDissertation Literature Review Template
Details
File Format
Size: 221 KB
DownloadSample Systematic Literature Review Template

Details
File Format
Size: 629 KB
DownloadPurpose of Literature Reviews
The basic goal of the literature review is summarizing and justifying the research. It also ensures neither the research analysis was done before nor it is a replication study. It provides a vast knowledge on the subject to the researcher. Also, it helps in tracking and figuring out the flaws associated or linked with the previous research. It helps in topic refining, refocusing, and changing the ongoing discussions. Also, it helps in marking the loops or gaps of previous research.
Target Audience
A literature review can be a thesis or a research paper essay. Many higher institutes and universities ask students to write literature reviews in the final year. It is practiced in almost all fields including arts, computer science, science, history, and social science etc. So, all university and college students can use our sample literature reviews for reference. It will help them in writing an effective research paper, dissertations, and thesis.
We are 100% assured that our above sample literature reviews have provided the essential help needed. Also, check our Performance Review Sample and conduct custom assessments easily. Please share few words with us by writing your suggestions, feedbacks, and queries in the comment box.
What are the 5 C’s of literature review?
Clarify the scope, Critique sources, Compare methodologies, Contextualize findings, and Connect to your research question to provide a comprehensive and insightful analysis of existing literature.
What is the purpose of writing a literature review?
The purpose is to summarize, synthesize, and critically evaluate existing research to identify gaps, establish a theoretical framework, and justify the need for your study.
What does a literature review look like?
A literature review is a structured summary and synthesis of existing research, organized thematically or chronologically, highlighting key findings, gaps, and the relevance to your research question.
How to do a literature review checklist?
Define scope, search for relevant literature, take detailed notes, organize findings thematically or chronologically, synthesize and critique sources, and ensure proper citation and formatting.
The literature review conclusively demonstrates the depth of existing research on the topic and identifies gaps for future study. It underscores the complexity of the subject and the ongoing need for further investigation to advance understanding and application. You can also see more on Research Paper Outlines.
If you have any DMCA issues on this post, please contact us
Related Posts
Visitors Log
Reflective Writing
Briefing Note
Timetable
Training Evaluation Forms
Acceptance Speech
Scientific Reports Samples & Templates
Attendance List Samples & Templates
Sample Meeting Minutes Templates
Presentation Speech Samples & Templates
Ukulele Chord Chart Samples & Templates
Retirement Speech Samples & Templates
Weekly Schedule Samples & Templates
Contractual Agreement Samples & Templates
FREE 9+ Amazing Sample Church Bulletin Templates in PSD | PDF
