Some businesses require more immediate attention than others. While every business wants their data to be as accessible as possible, organizations with a pressing need to restore data accessibility as soon as possible may need to invest more heavily in a system that meets their requirements. A data management plan should not be deemed complete until data availability issues have been appropriately addressed and managed. Redundancy is at the heart of much of what you need to know about data availability. When a system is designed to be redundant – that is, when backup systems are in place to take over in the event of a breakdown – it is significantly more capable of providing high availability.
4+ Data Availability Statement Samples
Data availability is a word used by computer storage manufacturers and storage service providers to define how data should be available at a certain degree of performance in a variety of conditions, from typical to disastrous. Data availability is generally achieved by redundancy in terms of where the data is stored and how it may be accessed. Some suppliers argue that a data center and a storage-centric philosophy and environment are more important than a server-centric philosophy and environment. The availability of information refers to its accessibility as well as its consistency. Data that isn’t easily accessible can stymie service delivery, costing an organization both time and money.
1. Data Availability Statement Sample
2. Printable Data Availability Statement
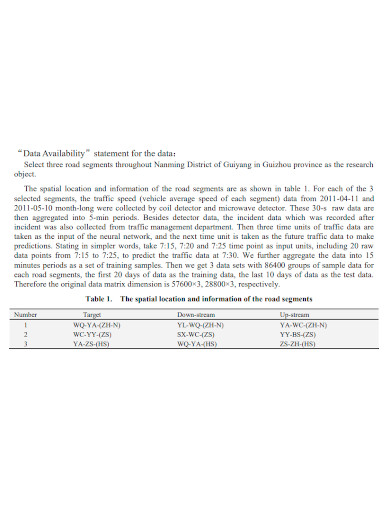
3. Standard Data Availability Statement
4. Data Availability Statement Analysis
5. Data Availability Statement Format
Maintaining data availability is critical to an organization’s success and business continuity. Your IT activities could grind to a halt if you lose access to mission-critical data, resulting in financial expenditures and, more critically, damage to your company’s reputation.
It is critical to understand what might cause your data to become unavailable and what hurdles you must face to safeguard your data in order to ensure its continuing availability and access. We’ll go through the fundamentals of data availability, as well as the issues it poses, and give ways to assist you maintain a high level of data availability.
Data Access
A user or data owner must be able to access and retrieve data stored in the network in order to use a company’s services. Organizations can provide certain people data access, allowing them to manage data. Data access can be sequential or random. Sequential data access allows users to access a data sequence in order, whereas random data access allows users to access any datum at any time. Data access is inextricably linked to data availability, which is reliant on the capacity to view, alter, and move data as needed.
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability Model
The CIA triad (confidentiality, integrity, and availability) is a paradigm that enterprises can use to establish their information security strategy and comply with data protection rules.
• Confidentiality—a collection of rules and processes aimed at preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data. Teaching security teams to discover vulnerabilities within the organization’s environment, training personnel to avoid data misuse, and implementing the usage of strong passwords are all examples of this.
• Data integrity – entails guaranteeing data accuracy, consistency, and dependability. Data integrity must be ensured both at rest and in transit, and security teams must take steps to assure this. File permissions, user access controls, and version controls are all protective measures against assaults that can modify data.
• Availability—the capacity to ensure consistent data access. Organizations must maintain critical data accessible at all times and minimize data outages as much as feasible. Organizations must be able to swiftly repair all hardware faults and maintain backups in order to achieve data availability.
FAQs
What is the difference between data durability and data retention?
Data durability is a separate but related goal from data availability, with a focus on the long term. Data availability is concerned with system uptime and operational live data, whereas data durability is concerned with data protection throughout its lifecycle. This involves ensuring that data isn’t corrupted or degraded. Data retention refers to data and records management rules that are kept for the purpose of analysis or compliance. Rather than being used immediately or frequently, the data is saved for later study or to give evidence in legal situations. A data retention policy directs data to be stored in a lower-level storage tier when it is not regularly accessed.
Why is it important to store back-ups?
Backups of your data should be kept in a second location or on a dispersed network. This assures that if a storage component fails or degrades, the data will not be permanently lost. You should update your backups on a regular basis so that you can restore the most recent copies of your data.
If you want to see more samples and formats, check out some data availability statement samples and templates provided in the article for your reference.
Related Posts
FREE 10+ Scholarship Statement of Purpose Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Engineering Problem Statement Samples [ Software, Mechanical, Civil ]
FREE 30+ Information Statement Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 50+ Policy Statement Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | PDF
FREE 50+ Summary Statement Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Nursing School Personal Statement in PDF
FREE 9+ Mortgage Statement Samples and Templates in PDF
FREE 10+ Independent Subcontractor Statement Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 10+ Trust Distribution Statement Samples in PDF
FREE 14+ Compliance Statement Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Extension Impact Statement Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Bank Reconciliation Statement Samples and Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Diversity Mission Statement Samples in MS Word | PDF
FREE 10+ Architecture Statement of Purpose Samples [ Sustainable, Graduate, Master ]
FREE 13+ Project Scope Statement Samples in PDF | MS Word