When you are going to come across researches in social sciences or even in humanities, you will notice that their research problems usually answers questions with “so what”. This type of question usually refers to surviving the quality of a measurement procedure. When you are going to answer questions having a “so what”, it simply implies that you don’t only have to show your available research materials, but also the thought of the significance of your research. In this article analysis, you will be able to know more about research problem statements and how to create a good one.
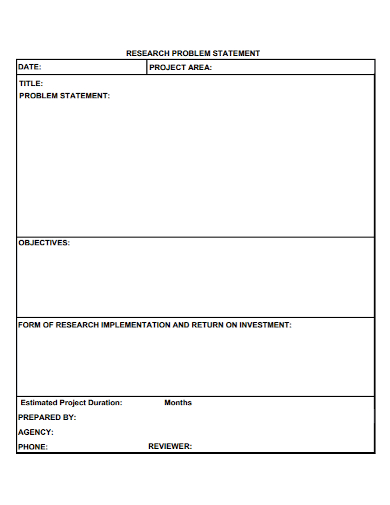
Research problem statement is defined as something that explains the problem in which your process improvement will address. In other words, it outlines all the negative points of the current situation and ultimately explains the reason why it actually matters. It is also a good tool used for communication which helps you in gaining total support from others. One of the major goals of a problem statement is to simply define the problem that is being addressed in a clear and precise manner. It focuses on the improvement of every processes and in steering every project scope.
Download Research Problem Statement Bundle
Research Problem Statement Related to Pediatric Nursing
There is a significant gap in the quality of pain management for pediatric patients in hospital settings, leading to inadequate pain relief and increased distress among young patients. Despite advances in medical protocols, many nurses face challenges in effectively assessing and managing pain in children due to limited specialized training, variations in pain expression among different age groups, and lack of standardized guidelines. This problem underscores the need for targeted education, improved assessment tools, and comprehensive pain management strategies to enhance the overall well-being and recovery of pediatric patients.
Background:
Pediatric patients often face unique challenges in pain management due to their developmental stages, which affect their ability to communicate pain effectively. Younger children may lack the verbal skills to describe their pain, while older children may underreport pain to avoid procedures or medications they fear. As a result, nurses must rely on observational skills and age-appropriate pain assessment tools, which may not always be accurate or consistently applied.
Current Challenges:
- Training and Education: Many nurses report insufficient training in pediatric pain management, leading to a lack of confidence in assessing and treating pain in children. Continuing education programs focusing on pediatric pain assessment and management are not universally available or mandated.
- Assessment Tools: Existing pain assessment tools, such as the FLACC scale (Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, Consolability) and the Wong-Baker FACES Pain Rating Scale, are useful but have limitations. These tools may not account for cultural differences in pain expression or the unique needs of children with communication difficulties or cognitive impairments.
- Standardized Guidelines: There is a lack of standardized guidelines across healthcare institutions for managing pediatric pain, leading to variability in care. This inconsistency can result in either over-treatment or under-treatment of pain, both of which have adverse effects on patient outcomes.
- Parental Involvement: Parents play a crucial role in managing their child’s pain but are often not adequately involved or informed about pain management strategies. Improved communication and collaboration between healthcare providers and parents are essential for effective pain management.
Research Objectives:
- To evaluate the effectiveness of current pediatric pain assessment tools and identify areas for improvement.
- To develop and implement a comprehensive training program for nurses focused on pediatric pain management.
- To establish standardized, evidence-based guidelines for pediatric pain management across healthcare settings.
- To explore strategies for better involving parents in the pain management process of their children.
Significance:
Improving pain management for pediatric patients is crucial for their physical and emotional well-being. Effective pain management can reduce the risk of chronic pain, improve recovery times, and enhance overall patient satisfaction. By addressing the gaps in education, assessment tools, guidelines, and parental involvement, healthcare providers can deliver more consistent and compassionate care to young patients.

Research Problem Statement in Nursing
Despite the critical role of nurses in patient care, there is a persistent issue of nurse burnout and job dissatisfaction, which adversely affects patient outcomes and healthcare quality. High levels of stress, inadequate staffing, and insufficient support contribute to physical and emotional exhaustion among nurses, leading to increased turnover rates and a strained healthcare system. This problem highlights the urgent need for effective strategies to improve nurse well-being, optimize staffing levels, and enhance workplace support to ensure sustainable and high-quality patient care.
Background:
Nurses are the backbone of the healthcare system, providing essential care and support to patients across various settings. However, the demanding nature of the job, characterized by long hours, high patient acuity, and emotional strain, often leads to burnout. Burnout is associated with symptoms such as fatigue, depersonalization, and a reduced sense of personal accomplishment, which can compromise patient care and increase the likelihood of medical errors.
Current Challenges:
- Staffing Levels: Many healthcare facilities struggle with inadequate nurse-to-patient ratios, leading to overworked nurses and decreased quality of care. Optimal staffing levels are critical for reducing burnout and ensuring patient safety.
- Workplace Support: Nurses often lack sufficient support from management and peers, which can exacerbate feelings of isolation and stress. Effective leadership and a supportive work environment are essential for nurse retention and job satisfaction.
- Professional Development: Opportunities for continuing education and professional growth are often limited, contributing to job dissatisfaction. Ongoing training and career advancement opportunities are important for keeping nurses engaged and motivated.
- Mental Health Resources: Access to mental health resources and programs for stress management is often inadequate. Providing comprehensive mental health support can help nurses cope with the emotional demands of their job.
Research Objectives:
- To evaluate the impact of nurse staffing levels on burnout and patient care quality.
- To develop and implement interventions aimed at enhancing workplace support and leadership in nursing.
- To assess the availability and effectiveness of professional development opportunities for nurses.
- To explore strategies for improving access to mental health resources and stress management programs for nurses.
Significance:
Addressing nurse burnout and job dissatisfaction is crucial for maintaining a robust healthcare system and ensuring high-quality patient care. By focusing on improving staffing levels, workplace support, professional development, and mental health resources, healthcare organizations can foster a more sustainable and fulfilling work environment for nurses. This, in turn, will lead to better patient outcomes, lower turnover rates, and a more resilient healthcare workforce.

Research Problem Statement in Medical Surgical Nursing
In medical-surgical nursing, there is a critical issue of suboptimal post-operative pain management, which leads to prolonged recovery times, increased risk of complications, and decreased patient satisfaction. Despite advances in pain management techniques, inconsistencies in pain assessment, inadequate patient education, and variations in pain management practices contribute to ineffective pain relief. Addressing this problem requires targeted interventions to standardize pain assessment protocols, enhance nurse education, and improve patient involvement in pain management strategies.
Background:
Medical-surgical nurses play a vital role in the care of patients undergoing surgical procedures, ensuring effective pain management is crucial for recovery and overall well-being. However, pain is often under-assessed and under-treated in the post-operative period, leading to adverse outcomes such as delayed mobilization, increased length of hospital stay, and higher healthcare costs. Effective pain management not only improves patient comfort but also reduces the risk of chronic pain development and enhances the overall recovery process.
Current Challenges:
- Inconsistent Pain Assessment: Variability in pain assessment practices among nurses can lead to inconsistent pain management. Standardized pain assessment tools and protocols are essential for ensuring accurate and consistent evaluation of pain levels.
- Inadequate Patient Education: Patients often receive insufficient education on pain management techniques and the importance of reporting pain accurately. Educating patients on pain management options and the significance of pain control is critical for effective pain management.
- Variability in Pain Management Practices: Differences in pain management practices among healthcare providers can result in unequal pain relief for patients. Establishing evidence-based guidelines and protocols can help standardize care and improve pain outcomes.
- Limited Nurse Education and Training: Nurses may lack specialized training in advanced pain management techniques, impacting their ability to provide effective pain relief. Ongoing education and training programs are necessary to equip nurses with the skills and knowledge needed for optimal pain management.
Research Objectives:
- To evaluate the effectiveness of current pain assessment tools and identify areas for standardization and improvement.
- To develop and implement educational programs for patients on post-operative pain management strategies.
- To establish evidence-based guidelines for pain management in medical-surgical settings and evaluate their impact on patient outcomes.
- To assess the effectiveness of nurse education and training programs in enhancing pain management skills and knowledge.
Significance:
Improving post-operative pain management in medical-surgical nursing is crucial for enhancing patient outcomes, reducing complications, and increasing patient satisfaction. By addressing the challenges of inconsistent pain assessment, inadequate patient education, variability in pain management practices, and limited nurse training, healthcare organizations can provide more effective and equitable pain relief. This, in turn, will lead to faster recovery times, reduced healthcare costs, and improved quality of life for patients undergoing surgical procedures.

Statement of the Problem Qualitative Research
In the medical-surgical nursing field, there is a significant gap in understanding the lived experiences and perspectives of nurses regarding the challenges of post-operative pain management. Despite technological and procedural advancements, nurses often encounter barriers that impede effective pain relief for patients. These barriers include inconsistencies in pain assessment, communication challenges with patients, and variations in pain management practices. Understanding these experiences qualitatively is essential to developing targeted interventions that can improve pain management practices and patient outcomes.
Background:
Medical-surgical nurses are crucial in managing post-operative pain, yet their experiences and perspectives are often underexplored. Effective pain management is not solely dependent on clinical skills but also on the ability to navigate the complex interactions with patients, healthcare teams, and institutional protocols. Exploring nurses’ lived experiences can provide deeper insights into the systemic and interpersonal factors that influence pain management practices.
Research Objectives:
- To explore the experiences and perspectives of medical-surgical nurses on post-operative pain management.
- To identify the barriers and facilitators that nurses encounter in assessing and managing post-operative pain.
- To understand the communication dynamics between nurses and patients regarding pain management.
- To explore nurses’ views on the adequacy of their training and institutional support in managing post-operative pain.
Research Questions:
- What are the lived experiences of medical-surgical nurses in managing post-operative pain?
- What barriers do nurses perceive in effectively assessing and managing post-operative pain?
- How do communication practices between nurses and patients impact pain management outcomes?
- How do nurses perceive the adequacy of their training and the support they receive from their institutions in managing post-operative pain?
Significance:
A qualitative exploration of nurses’ experiences with post-operative pain management can reveal the nuanced challenges and opportunities that quantitative studies might overlook. By understanding these experiences, healthcare administrators and educators can develop more effective training programs, create supportive institutional policies, and foster a culture of communication and collaboration that enhances pain management practices. Ultimately, this research aims to improve patient outcomes, nurse satisfaction, and overall healthcare quality in medical-surgical settings.

Browse More Templates On Research Problem Statement
1. Research Problem Statement Template
2. Sample Research Problem Statement Template
Problem statements must possess the following attributes: clarity and precision, identification of what needs to be studied, identification of the key factors and variables, identification of key concepts and terms, articulation of the boundaries and parameters of the research study plan, generalizability to making use of the results or outcome, conveyance of the importance of the research study, benefits, and justification, does not have jargons, and conveyance to gathering descriptive type of data.
3. Research Problem Purpose Statement Template
Process of Writing a Research Problem Statement

Step 1: Conceptualize the problem – the problem statement itself must be able to contain within our research problem and be able to provide a background on what should be known. For practical research, you should focus more on the details of the situation. For theoretical research, you should think about anything scientific, social, or a history background.
Step 2: Why it matters? – your problem statement should be able to address the importance of your research essay outline. What is more essential in this process is that you know exactly that it is researchable and feasible. For practical research problems, it should be relevant to the problem that directly affects the entire organization. For theoretical research problems, their relevance is not quite obvious.
Step 3: Know your objectives – ask yourself on how can you manage to address the problem. Your objective here is to seek for reasons behind the occurrence of the problem and propose effective and solid solutions.
Step 4: Review Existing Literature – Conduct a thorough review of existing literature to understand what has already been studied about your problem. This step helps identify gaps in the current knowledge and provides a foundation for your research. It also ensures that your problem statement is grounded in the context of existing research, which can enhance the credibility and relevance of your study. For practical research, focus on recent studies and reports that highlight the current state of the problem. For theoretical research, delve into foundational theories and frameworks that relate to your topic. You can also see more on Case Study Problem Statement.
Step 5: Define Scope and Delimitations – Clearly define the scope and delimitations of your research problem. This step involves specifying the boundaries of your study, including the population, settings, and variables you will focus on. It helps to narrow down the research problem to a manageable size and ensures that your study remains focused. For practical research, consider factors such as geographical location, specific practices, or population groups. For theoretical research, delineate the specific concepts, theories, or historical periods you will examine.
4. Sample Research Problem Statement Template
5. Research Problem Title Statement Template
6. Standard Research Problem Statement Template
7. Printable Research Problem Statement Template
When Should You Write a Problem Statement?
A problem statement should be written at the beginning of a research project or study, as it serves several critical functions that guide the entire research process. Here are the key times when you should write a problem statement:
- At the Start of a Research Project:
- Clarify Focus: Writing a problem statement at the outset helps clarify the focus and direction of your research. It ensures that you have a clear understanding of what you aim to investigate and why it is important.
- Guide Research Design: A well-defined problem statement guides the development of your research design, including the formulation of research questions, hypotheses, methodology, and data collection strategies.
- Align with Objectives: It aligns your research objectives and goals, ensuring that all aspects of your study are directed towards addressing the identified problem.
- When Seeking Funding or Approval:
- Grant Proposals: When applying for research funding, a clear and compelling problem statement is crucial. Funding bodies need to understand the significance of the problem you are addressing and how your research will contribute to solving it.
- Ethics Committees: When seeking approval from institutional review boards or ethics committees, a problem statement helps justify the need for your research and demonstrates its potential impact.
- During Proposal Development:
- Research Proposals: When developing a research proposal, a problem statement provides the foundation for your proposal document. It helps reviewers understand the context and importance of your research.
- Thesis/Dissertation Proposals: For academic research, such as theses or dissertations, a problem statement is essential for defining the research scope and ensuring that your study is focused and relevant.
- When Defining Research Scope:
- Scope and Boundaries: Writing a problem statement helps define the scope and boundaries of your research. It ensures that you remain focused on addressing the specific issue at hand and avoid straying into unrelated areas.
- Literature Review: It also informs the literature review process, helping you identify relevant studies and theories that relate to your research problem.
- In Collaborative Research:
- Team Alignment: In collaborative research projects, a problem statement helps align the research team around a common goal. It ensures that all team members have a shared understanding of the problem and the research objectives.
- Stakeholder Communication: It also facilitates communication with stakeholders, such as industry partners, policymakers, or community groups, by clearly articulating the problem your research aims to address. You can also see more on Management Problem Statement.
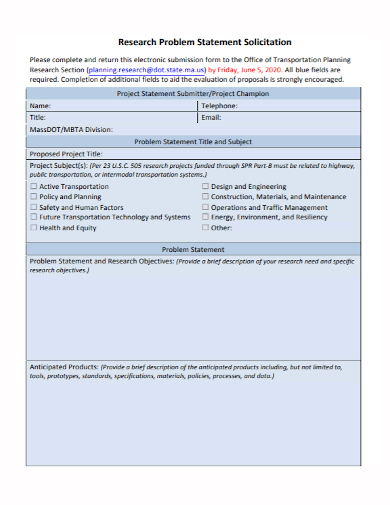
8. Research Solicitation Problem Statement Template
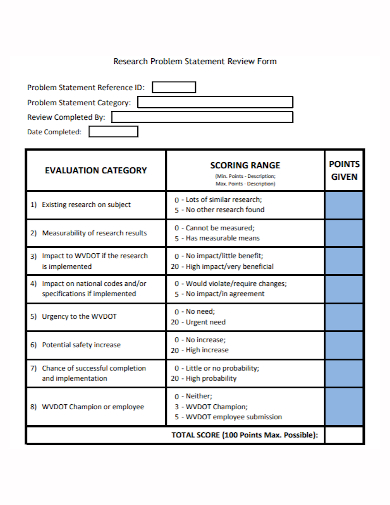
9. Research Problem Statement Review Form Template
Important Features of Research Problem Statement
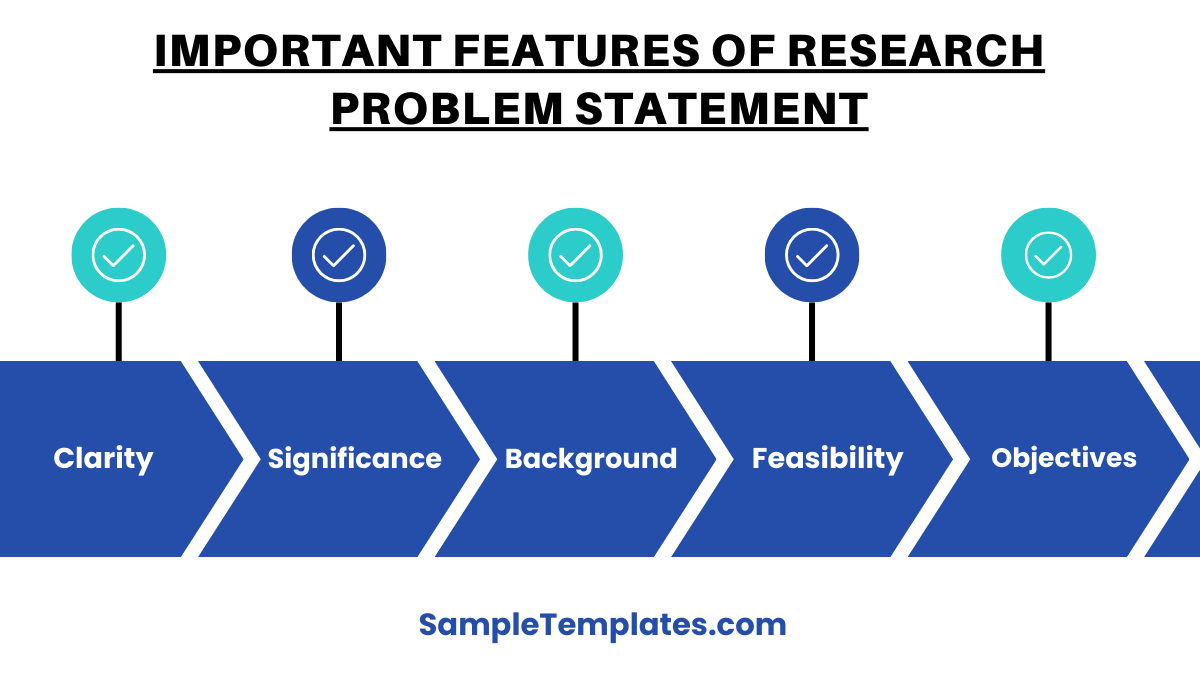
- Clarity and Precision:
- The problem statement should be clearly articulated and precisely defined. It should avoid ambiguity and be specific about the issue being addressed.
- Significance and Relevance:
- It should highlight the importance of the problem and its relevance to the field of study. The sample statement should explain why the problem is worth investigating and how it impacts the subject area.
- Context and Background:
- Provide sufficient context and background information to help readers understand the problem’s setting. This includes any historical, social, or scientific context necessary to frame the issue.
- Research Gap Identification:
- The problem statement should identify gaps in existing knowledge or areas where current understanding is lacking. This demonstrates the need for the proposed research.
- Feasibility:
- It should indicate that the problem is researchable and feasible within the constraints of time, resources, and scope. The problem should be something that can be realistically investigated.
- Specific Objectives:
- The problem statement should include specific research objectives or questions that the study aims to address. These objectives guide the direction and focus of the research.
- Impact and Implications:
- It should outline the potential impact and implications of addressing the problem. This includes potential benefits, applications, or contributions to theory, practice, or policy.
- Alignment with Methodology:
- The statement should be aligned with the proposed research methodology. It should hint at the approach or methods that will be used to investigate the problem, ensuring coherence between the problem and the research design. You can also see more Report Problem Statement.
10. Statement of Research Problem Template
11. Sample Research Proposal Problem Statement Template
12. Editable Research Problem Statement Template
Example Research Problem Statement
“The staffing model in the Process Improvement Unit (PIU) has changed (we have more staff, and some of the staff have different working patterns) we need to have a clear way of recording status and stage of our business activities (projects, workshops and training) that will be used by all PIU staff, so that we can work effectively and provide good service to our customers. A member of staff is due to go on annual leave in two weeks time and we have no visibility or way of easily sharing information about their work analysis, this will make it hard for the rest of the team to cover the work during staff absence.”
sheffield.ac.uk
FAQs
What is the criteria when reviewing for your problem statement?
It should only focus on one problem, should be 1-2 sentences long, and should not suggest a solution.
What should an effective problem statement do?
It puts the problem in the context, describe the present issue, show the importance of the problem, and set the objectives for your research.
If you want to see more samples and format, check out some of the research problem statement samples and templates provided in the article for your sample reference.
Related Posts
FREE 10+ Research Worksheet Samples
FREE 10+ Analytical Thesis Statement Samples
FREE 10+ Educational Impact Statement Samples
FREE 10+ Internship Statement of Purpose Samples
FREE 10+ Product Compliance Statement Samples
FREE 10+ Safe Work Method Statement Samples
FREE 10+ Community Impact Statement Samples
FREE 5+ Employee Impact Statement Samples
How to Write a A+ Research Paper?
FREE 36+ Statement Examples & Templates
FREE 28+ Statement Samples
FREE 10+ Construction Method Statement Samples
FREE 10+ Graduate Statement of Purpose Samples
FREE 8+ Research Agenda Samples
FREE 10+ Human Resource Statement of Purpose Samples