A feature story targets to educate and entertain readers. It brings out the best in a writer. It can be personal, colorful, and assertive, but without drifting from the truth. It may be longer and in-depth compared to an easy article analysis. Feelings are carried here. Have a look at the feature writing samples provided down below and choose the one that best fits your purpose.
Download Feature Writing Bundle
What is the purpose of feature writing?
One essential and important writing material is a feature article. Features are more in-depth than traditional news stories and go beyond giving out the most important facts. The objective of these stories is to provide a detailed description of a place, person, idea, or organization.
Format of Feature Writing
1. Headline
- Captivating and Descriptive: Draws readers in with intrigue or emotion, hinting at the story’s theme or focus.
2. Subhead (Optional)
- Additional Context: Provides more detail about the feature’s content, complementing the headline.
3. Lead (Lede)
- Engaging Opening: A compelling introduction that sets the tone, introduces the topic or main characters, and hooks the reader. It can be anecdotal, descriptive, surprising, or pose a question.
4. Nut Graf
- The Essence: Located after the lead, this paragraph gives the story’s thesis or main idea, explaining why the story matters and what it will cover.
5. Body
- Development: The story unfolds in a structured, engaging manner. This section is often segmented into several parts, including:
- Background Information: Contextual details that help the reader understand the subject’s significance.
- Main Narratives: The core stories, arguments, or descriptions that drive the feature.
- Supporting Evidence: Data, quotes from interviews, research findings, and expert opinions that lend credibility and depth.
- Themes: Recurring ideas or motifs that tie different parts of the story together.
- Transitions: Smooth and logical connections between different sections, maintaining flow and coherence.
6. Direct Quotes
- Voices of the Story: Incorporate firsthand insights from key figures or experts to add authenticity, perspective, and emotion.
7. Imagery and Descriptions
- Vivid Detailing: Use descriptive language to paint pictures in the reader’s mind, making the story memorable and immersive.
8. Conclusion
- Reflective Closure: Wraps up the story satisfyingly, often tying back to the lead, reflecting on the story’s implications, or looking to the future. It should leave a lasting impression on the reader.
9. Sidebar (Optional)
- Additional Information: Boxes or sidebars that include related information, statistics, timelines, or mini-profiles complementing the main narrative.
10. Call to Action (Optional)
- Engagement: Encourages readers to engage further with the topic, whether through social media, further reading, or personal reflection.

Feature Writing For Students
Feature writing is an exciting way for students to explore storytelling, combining factual reporting with narrative techniques to engage readers deeply. Whether you’re covering a school event, profiling a notable person in your community, or exploring a significant issue, feature articles allow you to delve into the subject matter with creativity and depth. Here’s a simple guide to help students craft compelling feature stories.
Choosing a Topic
- Interest and Relevance: Pick a subject that fascinates you and is relevant to your audience.
- Unique Angle: Find a unique perspective or an untold aspect of a well-known story to stand out.
Research and Interviews
- Comprehensive Research: Gather detailed information about your topic from reliable sources.
- Interviews: Talk to people directly involved or knowledgeable about your subject to add depth and authenticity to your story.
Writing Your Feature
1. Headline
- Create an engaging headline that captures the essence of your story and piques curiosity.
2. Lead (Lede)
- Start with a strong opening that grabs attention. Use an anecdote, a striking fact, or a compelling question.
3. Nut Graf
- After your lead, include a paragraph that explains the significance of your story and what it will cover.
4. Body
- Structure: Organize your article into clear, logical sections. Use headings if necessary.
- Main Content: Develop your narrative, integrating background information, anecdotes, and insights from your interviews.
- Quotes: Incorporate direct quotes to add voice and perspective.
- Descriptive Detail: Use vivid descriptions to bring scenes and personalities to life, making your story engaging and immersive.
5. Conclusion
- Conclude your feature with a strong closing that leaves a lasting impression. You can circle back to your opening or end with a thought-provoking statement or question.
Tips for Effective Feature Writing
- Show, Don’t Tell: Use specific examples and descriptions to show your readers what you mean, rather than simply telling them.
- Voice and Tone: While maintaining accuracy, don’t be afraid to let your voice shine through, making your writing more relatable and enjoyable.
- Engage the Senses: Include details that engage the readers’ senses, making your story more vivid and memorable.
- Revise and Edit: Review your work critically, checking for clarity, coherence, grammar, and spelling. Ask for feedback from peers or teachers.

Feature Writing about a Person
Title
- Engaging and Descriptive: Captures the essence of the person and piques curiosity.
Subtitle (Optional)
- Further Insight: Provides additional context or highlights a key aspect of the person’s story.
Introduction
- Hook: Start with an engaging anecdote, quote, or moment that draws the reader in and introduces the person’s character or significance.
- Context: Briefly introduce the person, including their name, known for, and why they are noteworthy.
Background
- Early Life: Share insights into their upbringing, education, and any formative experiences that shaped their path.
- Career Path: Outline their career journey, noting key turning points, achievements, and challenges faced.
Main Body
- Characteristics: Describe their personality traits, values, and qualities that stand out.
- Contributions and Impact: Highlight their accomplishments, work, or contributions to their field, community, or society.
- Challenges Overcome: Discuss any obstacles they faced and how they overcame them, illustrating resilience and determination.
- Personal Anecdotes: Include stories or moments that reveal their character, preferences, and everyday life.
- Quotes: Incorporate direct quotes from the person, and possibly from colleagues, friends, or family, to provide diverse perspectives and authenticity.
Themes
- Central Themes: Identify and weave through recurring themes or messages, such as innovation, leadership, perseverance, or community service, that are relevant to their story.
Imagery
- Visual Elements: Use photographs or illustrations that capture the person in different aspects of their life or work, adding depth to the narrative.
Conclusion
- Reflective Closure: Summarize their legacy or impact and reflect on what readers can learn from their story. Consider ending with a powerful quote from or about the person that encapsulates their essence.
Sidebar (Optional)
- Key Achievements: A list or timeline of significant milestones or accolades.
- Further Reading: References to their work, interviews, or other materials for readers who wish to explore more.

Feature Writing For Elementary Students
Title
- Simple and Fun: Use clear, catchy titles that hint at the adventure or learning journey ahead.
Introduction
- Start with a Bang: Begin with an exciting fact, question, or short story to grab their attention.
- Introduce the Subject: Clearly state what or who the feature is about in a way that’s easy for children to understand.
Main Body
- Use Simple Language: Write in straightforward, age-appropriate language, avoiding complex terms or jargon.
- Incorporate Characters: If possible, present information through the experiences of characters they can relate to or admire.
- Engaging Format: Use short paragraphs, bullet points, and lots of subheadings to break up text and make it easier to digest.
- Visual Elements: Include colorful images, drawings, or diagrams to illustrate points and add visual interest.
- Educational Content: Weave in learning moments naturally, such as interesting facts or life lessons, without making it feel like a traditional lesson.
- Interactive Elements: Suggest activities, questions for reflection, or simple experiments related to the topic to encourage active engagement.
Conclusion
- Wrap Up with a Highlight: Summarize the key points or the moral of the story in a memorable way.
- Encourage Curiosity: End with a question or a teaser about another interesting fact or story, motivating them to learn more on their own.
Sidebar (Optional)
- Glossary: Explain any difficult words used in the article.
- Did You Know?: A box with fun facts related to the feature’s topic.

Fact Sheet For Feature Writing
Purpose of Feature Writing
- Engage: Capture the reader’s interest with a story that is more in-depth than a basic news report.
- Inform: Provide comprehensive background information, context, and details about the topic.
- Persuade: (Optional) Sway readers’ opinions or encourage them to take action, depending on the feature’s aim.
- Entertain: Offer an enjoyable reading experience through storytelling techniques.
Key Components
- Headline: Captivating and summarizing the essence of the story.
- Lead (Lede): An opening paragraph that hooks the reader, often with an anecdote, striking fact, or question.
- Nut Graf: A paragraph that outlines the central theme or purpose of the story, providing a roadmap for what’s ahead.
- Body:
- Background Information: Essential details that set the scene or provide context.
- Development: The story’s main content, including arguments, descriptions, and narratives.
- Supporting Elements: Quotes, statistics, anecdotes, and examples that enrich the narrative.
- Conclusion: Wraps up the story, often tying back to the lead or looking forward to the future.
- Call to Action: (Optional) Directs readers toward further engagement or exploration of the topic.
Types of Feature Articles
- Profile: Focuses on an individual’s life, achievements, and character.
- Trend: Explores current movements or shifts in society, culture, or industry.
- Issue: Investigates a particular problem or topic, offering in-depth analysis.
- Human Interest: Tells a story that appeals to emotions, showcasing personal experiences or challenges.
- How-To: Provides step-by-step guidance on completing a task or solving a problem.
Writing Style and Techniques
- Narrative Flow: A well-structured narrative that guides the reader through the story.
- Descriptive Language: Vivid descriptions that engage the senses, painting a picture for the reader.
- Active Voice: Keeps the writing dynamic and direct.
- Variety of Sentence Structures: Enhances readability and maintains the reader’s interest.
- Direct Quotes: Adds authenticity and perspective.
Research and Preparation
- Thorough Research: Gather detailed information from reliable sources to ensure accuracy.
- Interviews: Conduct interviews with relevant individuals to add depth and authenticity.
- Fact-Checking: Verify all facts, quotes, and details to maintain credibility.
Ethical Considerations
- Accuracy: Commit to truth and accuracy in all aspects of the story.
- Fairness: Present a balanced view, especially when covering controversial topics.
- Respect: Treat all subjects and sources with respect and consideration.
Visuals and Graphics (Optional)
- Photographs: Enhance the story and provide visual interest.
- Infographics: Offer a visual representation of data or concepts.
- Videos: (For online features) Add an engaging multimedia element.
Conclusion
Feature writing is an art that combines factual reporting with creative storytelling to produce an engaging and informative piece. By following these guidelines, writers can craft stories that resonate with their audience, providing depth and insight into a wide range of topics.

Browse More Templates On Feature Writing
Feature Writing Template
Feature writing in journalism escapes the hard-news format permitting the creative writers among us to write feature articles in a creative and captivating way. Unlike short and accurate news articles, feature articles deal with a subject in greater depth and, generally, at greater length. Check out the writing sample template here which consists of guidelines, requirements and course overview on feature writing of journalism. This file has been provided in word file so you can simply edit or modify the entire document as you want to. Download it now to get started.
How Does Feature Writing Differ from News Writing?
| Feature Writing | News Writing |
|---|---|
| Explores in-depth stories and analysis | Focuses on reporting facts quickly |
| Emphasizes storytelling and narrative | Prioritizes timeliness and brevity |
| Provides context and background | Presents information objectively |
| Evokes emotions and engages the reader | Aims for a straightforward delivery |
| Can be more subjective and expressive | Requires a more neutral tone |
| Often has a longer, more elaborate form | Typically has a concise and direct form |
| Includes human interest and anecdotes | Prioritizes the latest and essential news |
| Allows for creative expression | Follows a standardized news format |
Example of Feature Writing in Journalism
A unit on Journalism: Feature Writing has been provided in this sample for your reference. This unit is designed to allow the learner to attain the key skills that a journalist needs for writing features — researching, structuring and writing feature articles for newspapers, magazines, sample websites and other online sources. On successfully completing the unit you will be able to write and pitch feature synopses, research and write articles based on secondary sources, and research and write articles based on primary and secondary sources. Download it now to make your task easy and hassle-free.
How to Begin Writing a Feature Article?
- Choose a Compelling Angle: Select an intriguing aspect or angle that captures readers’ interest.
- Thorough Research: Conduct in-depth research to gather relevant information and insights.
- Create a Strong Lead: Craft a compelling introduction that hooks readers and sets the tone for the entire piece.
- Define the Narrative Structure: Sample Outline a clear structure with a captivating beginning, engaging middle, and a satisfying conclusion.
- Highlight Human Elements: Incorporate personal stories, experiences, or interviews to add a human touch.
- Use Descriptive Language: Employ vivid and descriptive language to create a sensory experience for the reader.
- Consider Your Audience: Tailor the tone and style to resonate with the target audience.
- Show, Don’t Just Tell: Use anecdotes, examples, and storytelling techniques to convey information in a vivid and engaging manner.
Feature Writing Template
A syllabus on journalist feature writing is presented here in the template to teach students how to interest readers insignificant, research-based subjects by writing about them in the context of non-fiction stories that have characters, show development and follow a structural arc from beginning to end. It consists of course description, learning objectives, suggested & recommended reading, assignments, methodology, and weekly schedule and exercises. Help yourself by downloading this template for free.
Principles of Feature Writing
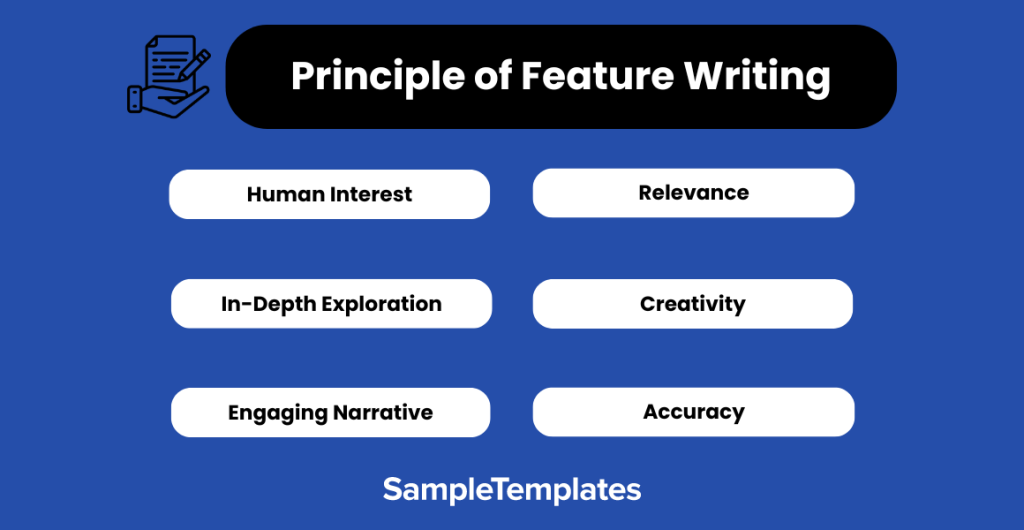
- Human Interest: Prioritize stories that evoke emotions or resonate with readers on a personal level.
- In-Depth Exploration: Go beyond surface details, providing comprehensive context and sample analysis.
- Engaging Narrative: Craft a compelling and well-structured story with a strong beginning, middle, and end.
- Relevance: Choose topics that are timely, interesting, and meaningful to your audience.
- Creativity: Embrace creativity in language use, storytelling techniques, and presentation.
- Accuracy: Thoroughly research and fact-check to maintain credibility and trustworthiness.
- Diversity of Voices: Incorporate different perspectives and voices to enrich the narrative.
- Reader Connection: Aim to establish a strong connection between the reader and the subject matter.
Feature News Writing Format
Get helpful hints for sample journalistic writing in this sample. You will learn the basics of news writing like hard news, feature writing like soft news, and review writing. Your work will be a lot easier and simple if you download this template and go through the details provided.
What is the Main Objective of Feature Writing?
The main objective of feature writing is to transcend traditional news reporting, offering readers a deeper understanding and emotional connection to a subject. Feature articles aim to entertain, inform, and engage by employing storytelling techniques, vivid descriptions, and human elements. These narratives explore diverse topics, providing context, analysis, and personal perspectives. Unlike news articles, the primary goal list is not just to convey facts but to evoke emotions, provoke thought, and create a lasting impact on the reader. Feature writing aims to captivate, inspire, and foster a connection between the audience and the subject matter.
Magazine and Feature Writing Template
The process of writing a feature article for a magazine is not much different from writing an article for a newspaper or newsletter. Magazine writing lies between a piece of fiction and the main news reporting. The magazine article can have all the entertainment value of fiction, using plot, scenes, characters, and description. At the constant time, the magazine journalist presents interesting, topical information – hard facts gained from research and interviews. Feature writing imitates the novel in that it pays direct attention to information that would be considered not necessary and inappropriate in newspaper journalism. Yet, the details included are relevant, entertaining, to the point, and written in the short sentences that epitomize most good journalism. Given here is a sample on magazine and feature writing which you can take reference from.
Structure of Feature Writing
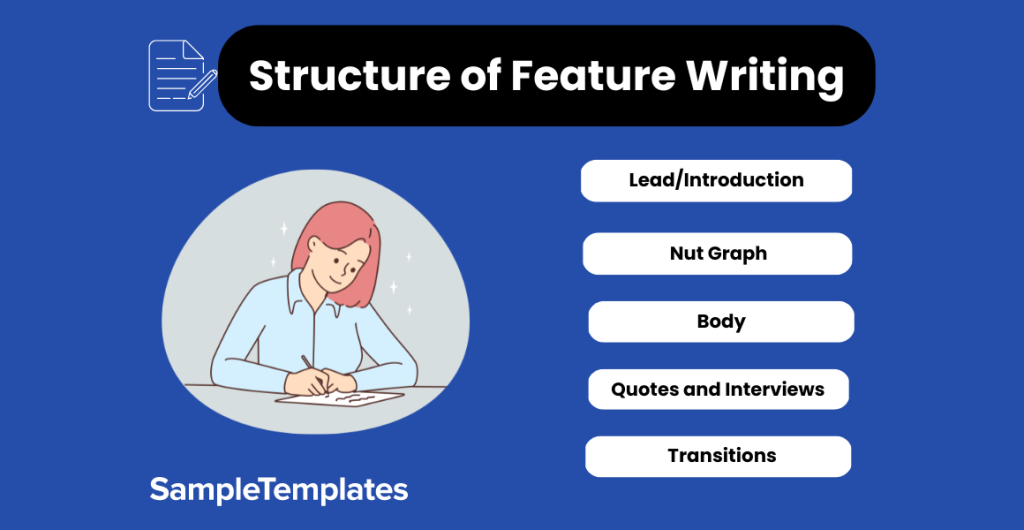
- Lead/Introduction: Capture attention with a compelling opening that introduces the main idea or theme.
- Nut Graph: Provide a concise summary of the article’s focus, outlining its significance.
- Body: Develop the story with supporting details, anecdotes, and in-depth information.
- Quotes and Interviews: Incorporate direct quotes and insights from relevant sources or interviews.
- Transitions: Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs and sections for a cohesive flow.
- Conclusion: Summarize key points and leave a lasting impression, possibly with a thought-provoking closing statement.
- Call to Action (if applicable): Encourage readers to reflect, take action, or explore the topic further.
Reporting and Feature Writing in PDF
The major distinction between a news article and a feature story is that a news article is time-sensitive.
Media retailers wish to publish news stories as quickly as doable when an incident happens. Feature stories, however, aren’t as time-dependent and contain no pressing content. In this PDF file along with the checking of report writing format learn what Reporting & Feature Writing is gain knowledge and information about it.
What is Feature Writing and its Types?
- Profile Features: Highlighting individuals, their stories, and contributions.
- Human Interest Features: Evoking emotions by focusing on unique or touching aspects of life.
- Explanatory Features: Providing insights and analysis to explain complex issues or phenomena.
- In-Depth Interviews: Presenting detailed conversations with notable figures or experts.
- Travel Features: Describing destinations, cultures, and experiences in a narrative format.
- Historical Features: Exploring events, trends, or personalities from the past with depth and context.
Feature Writing Template
Feature stories are descriptive and full of detail. Feature stories generally have a strong narrative line. Feature stories have a powerful lead that grabs audiences and makes them wish to read on. Feature stories include sample quotations from the person(s) involved. Check out the example given here which will make your concept clear and will permit you to get enough reference from it.
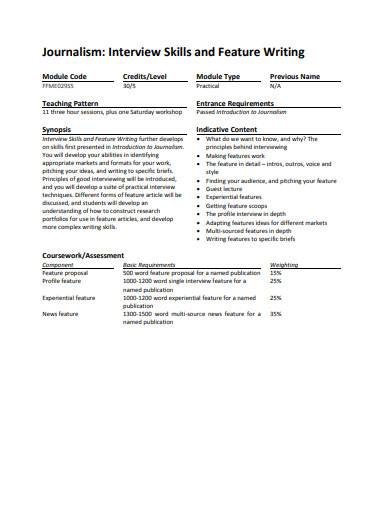
Interview Skills and Feature Writing Template
In this template, you will learn about Journalism: Interview Skills and Feature Writing. Interview Skills and Feature Writing further develops on skills first presented in Introduction to Journalism. Here, you will develop your abilities in identifying appropriate markets and formats for your work, pitching your ideas, and writing to specific briefs. Take a look at it now to get started.
What are the Sources of Feature Writing?
- Interviews: Direct conversations with individuals involved in or knowledgeable about the topic.
- Observation: Firsthand experiences and observations provide authenticity and depth.
- Research: Utilize books, articles, and reliable online sources to gather background information and context.
- Data and Statistics: Incorporate relevant statistics or data to support your narrative.
- Personal Experiences: Share your own experiences or reflections if applicable.
- Experts and Authorities: Quotes or insights from experts add credibility to the narrative.
- Visuals: Include photographs, illustrations, or multimedia elements to enhance storytelling.
- Archives and Historical Data: Explore archives or historical records for context and depth.
- Surveys and Polls: Use survey data or public opinions to strengthen your narrative.
Formal Feature Writing Template
A course on formal feature writing has been assigned here. This course focuses on journalistic reporting and writing for a variety of media, including online and print newspapers and magazines, broadcast television and radio, as well as online-only and social media platforms. Download it now to attain more information about it.
What is feature writing and examples?
Feature writing is a form of journalism that explores and elaborates on specific aspects of a story, going beyond the basic facts to provide in-depth analysis, background information, and human interest elements. Here are examples of feature writing:
- Profile Feature:
- Example: A profile on a successful entrepreneur, delving into their journey, challenges faced, and lessons learned.
- Human Interest Feature:
- Example: A heart warming story about a community coming together to support a local family in need.
- Investigative Feature:
- Example: An in-depth investigation into environmental issues, uncovering the impact of industrial activities on a local ecosystem.
- Behind-the-Scenes Feature:
- Example: A look behind the scenes of a popular TV show, revealing the creative process and challenges faced by the production team.
- Historical Feature:
- Example: An exploration of a historical event, providing context, personal stories, and its relevance to the present.
- Travel Feature:
- Example: A travel piece capturing the unique culture, cuisine, and experiences of a particular destination.
- Opinion Feature:
- Example: An op-ed piece discussing a pressing social or political issue, offering a unique perspective and potential solutions.
- Trend Analysis Feature:
- Example: An examination of current trends in technology, fashion, or entertainment, exploring their impact on society.
- Inspirational Feature:
- Example: A story highlighting the achievements and resilience of individuals who have overcome significant challenges.
- Cultural Feature:
- Example: An exploration of a cultural tradition or phenomenon, shedding light on its significance and evolution over time.
Feature writing allows for creativity and storytelling, often combining elements of narrative, research, and interviews to provide readers with a richer understanding of a subject.
What is Feature Writing?
Feature writing is a journalistic style that delves deeply into a topic, weaving facts, storytelling, and analysis. It goes beyond the who, what, when, and where, providing context, emotion, and insight.
Can Feature Writing Include Opinion?
Feature writing, while rooted in facts, can include the writer’s opinion to add depth and personal insight. This subjective touch enhances the narrative, making it more engaging and relatable.
Is Feature Writing Only for Journalists?
Feature writing isn’t exclusive to journalists; anyone passionate about storytelling can engage. Bloggers, authors, or individuals sharing experiences can delve into feature writing, utilizing creativity to captivate and inform readers.
What Impact Can Feature Writing Have?
Feature writing holds the power to inspire, inform, and evoke emotional responses. Through engaging narratives and in-depth exploration, it forges a meaningful connection between the reader and the subject matter.
How Long Should a Feature Article Be?
Feature articles vary in length, but they are generally longer than traditional news pieces, allowing for a more in-depth exploration of the subject.
In conclusion, feature writing adds depth and context to stories, offering readers a richer and more nuanced understanding of the subjects explored. Through creativity and in-depth analysis, feature writing goes beyond the facts, providing a compelling and engaging narrative.
Related Posts
Writing Termination Letters Due to Poor Performance
6+ Business Profile Samples
15+ SOAP Note Examples
8+ Sample Accounting Memo Documents
FREE 7+ Commentary Writing Samples
FREE 9+ Story Outline Samples
What Is Incident Report in Software Testing?
How to Write a Navy Standard Operating Procedure
FREE 6+ Printable Writing Paper Templates
How to Write a Captivating Recommendation Letter for Employment ...
FREE 10+ Congratulation Letters
Sample Job Proposal Template
FREE 14+ Sample Variances Templates
4 Data Entry Cover Letters
Sample Letter of Interest